10.1002/anie.200801675
The study provides conclusive evidence for an SN2-Si mechanism in the B(C6F5)3-catalyzed hydrosilylation of carbonyl compounds, which has implications for the related hydrogenation reactions. The researchers used a silane with a stereogenic silicon center as a stereochemical probe to investigate the transition state in the B(C6F5)3-catalyzed hydrosilylation of prochiral acetophenone. They found that the reaction proceeds through a concerted SN2-type displacement at silicon, involving a four-centered cyclic transition state, rather than through a free silylium ion intermediate. This mechanistic understanding is significant for the development of catalytic asymmetric approaches and could guide the design of novel processes in synthetic chemistry. The study also suggests that the efficiency of such reactions may depend on the asymmetric induction of a chiral nonracemic borane catalyst.
10.1021/jo00116a042
The research focuses on the synthesis and solid-state structure of substituted arylphosphine oxides, which are of interest due to their potential as second-order nonlinear optical materials. The study aimed to prepare and characterize new arylphosphine oxides with donor and acceptor substituents, exploring the influence of hydrogen bonding on their propensity to form acentric crystals, crucial for their use in nonlinear optical materials.
10.1134/S1070363207120110
The research investigates the kinetics of photolytic transformations of 4,4'-Bi(3-methyl-6-tert-butyl-o-benzoquinone) (Q-Q) in hydrocarbon solutions under light with wavelengths of 313 and 405 nm. The study aimed to determine the quantum yields and apparent rate constants of the photolysis process and suggest a probable scheme of photochemical reactions. The researchers identified two main pathways for Q-Q transformation under irradiation: reduction via abstraction of hydrogen atoms from a solvent molecule to form bi(5-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-2-methylcyclohexa-2,5-dien-4-one-1-ylidene) (IA), and decarbonylation yielding 6-tert-butyl-4-(4-tert-butyl-2-methyl-3-oxocyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)-3-methyl-o-benzoquinone (IB).


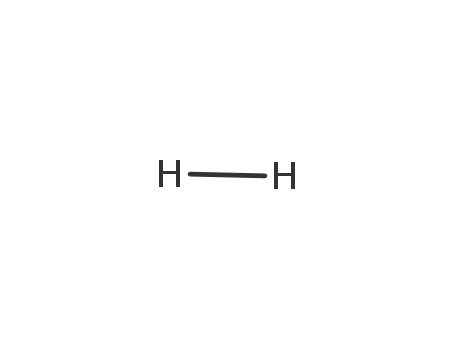
 F+
F+


