10.1021/jo961653u
The study focuses on the total synthesis of (±)-dihydrokawain-5-ol, a unique natural product isolated from the kava plant (Piper methysticum). The synthesis begins with a highly diastereoselective iodocyclofunctionalization of α-allenic alcohols to produce vinyl iodo syn-vicinal diols. A key feature of the synthesis is the differentiation of the alcohol groups in the vicinal diols through selective monoprotection using methoxymethyl (MOM) ethers or silyl ethers, followed by further functional group manipulations. The work explores various regioselective monoprotection techniques, cyclization strategies, and the isomerization of intermediates to form the final dihydropyranone structure found in dihydrokawain-5-ol. The study exemplifies the challenges and solutions in synthesizing complex natural products with specific stereochemical requirements.
10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.10.013
The research focuses on the discovery and structure-activity relationship (SAR) of a novel series of spirocyclic renin inhibitors for the treatment of hypertension. The study aimed to enhance renin potency and reduce hERG affinity and CYP3A4 inhibition through spirocyclization, which restricts the molecule to its bioactive conformation. Experiments involved the synthesis of various spirocyclic compounds, with compound 31 identified as an optimized renin inhibitor. Reactants used in the synthesis included 2-bromo-4,5-difluorobenzoic acid, TBSCl, imidazole, DMF, Pd(dppf)Cl2, Na2CO3, and other reagents for Suzuki coupling and cyclization reactions. Analytical methods employed in the study included buffer and plasma renin inhibition assays, hERG channel affinity measurements, and CYP3A4 inhibition assessments, which were used to evaluate the potency, safety, and metabolic profile of the synthesized compounds.
10.1248/cpb.34.423
The research aimed to develop a facile synthesis method for 6,3'-methanouridine and 6,3'-methanocytidine, which are nucleosides with a methylene group bridging the C-6 of the sugar and the 3'-position of the pyrimidine base. These compounds are of interest for their potential biological and pharmacological properties. The synthesis involved the condensation of 2,4-dimethoxy-6-lithiomethylpyrimidine with 5-O-(tert-butyldimethyl)silyl-1,2-O-isopropylidene-3-ketoxylose, followed by intramolecular glycosylation and deprotection steps. Key chemicals used in the process included 1,2-O-isopropylidene-D-xylose, t-butyldimethylchlorosilane, chromium trioxide, tetrahydrofuran (THF), and various protecting groups such as t-butyldimethylsilyl and benzoyl groups. The researchers concluded that their method was effective for the large-scale preparation of 6,3'-methanouridine and related compounds of biochemical interest.
10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.07.074
The study presents the first total synthesis of greensporone C, a cytotoxic 14-membered resorcylic acid lactone with potential biological activities such as cytotoxicity against certain cancer cell lines. The synthesis involved a 16-step linear sequence with a 3.3% overall yield. Key chemicals used in the study include Mitsunobu reagents for esterification to construct the macrocycle and establish the (E)-olefin geometry, benzoic acid derivatives and (R)-non-8-en-2-ol as key fragments for the synthesis, and various protecting groups and reagents such as ethoxymethyl (EOM), t-butyldimethylsilyl chloride (TBSCl), and iodobenzene diacetate for protecting and modifying functional groups. The purpose of these chemicals was to construct the complex structure of greensporone C, confirm its absolute stereochemistry, and potentially unlock its biological activities for further study and application.
10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2011.03.005
The research focuses on the synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the cytotoxic activity of a series of cobalt(II) β-ketoaminato complexes towards various human tumor cell lines. The purpose of the study was to investigate the potential of these cobalt compounds as novel cytotoxic drugs, selective towards certain types of tumors. The researchers prepared a series of square planar cobalt(II) compounds with tetradentate β-ketoaminato ligands, varying in the number of ―CF3 ligand substituents, and one tetrahedral cobalt compound with two bidentate ligands. The compounds were synthesized using a multistep reaction sequence involving chemicals such as CoCl2, sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide, sodium hydride, tert-butyldimethylchlorosilane, 1,2-diaminoethane, and various β-diketones, including hexafluoroacetylacetone and 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-phenyl-1,3-butanedione. The conclusions drawn from the study indicate that the cobalt complexes, particularly L2Co, exhibit significant cytotoxic activity against prostate cancer and leukemia cells, with activity mediated through mechanisms involving caspase-3, MAP kinases, and reactive oxygen species. These findings suggest that these cobalt complexes could be developed as a new class of cytotoxic drugs.
10.1139/v80-010
The study investigates the preparation, characterization, and reactions of N-tert-butyldimethylsilyl derivatives of various heterocyclic compounds, including imidazole, 2-methylimidazole, 4-methylimidazole, benzimidazole, pyrazole, 1,2,4-triazole, and benzotriazole. These derivatives were synthesized using tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride and the corresponding heterocyclic compounds. The products were identified and characterized using carbon and proton nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis. The study confirmed the absence of intermolecular silyl exchange at ambient temperature through carbon NMR spectra, but noted that such exchange occurred at elevated temperatures (130-160°C). The study also explored the reaction of these silyl derivatives with dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), resulting in the formation of N-(methylthio)methyl derivatives of the heterocycles. The mechanism for this reaction involves a Pummerer rearrangement, and the products were characterized using various analytical techniques, providing insights into the stability and reactivity of these compounds under different conditions.


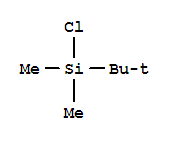
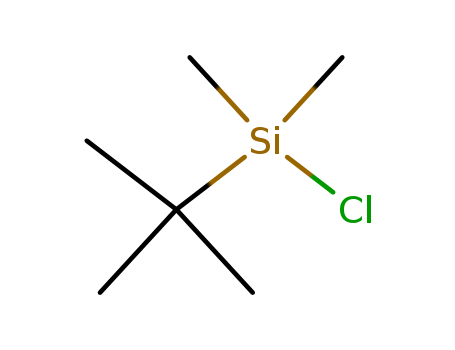
 C,
C, F,
F, T
T


