10.1021/acscatal.0c05372
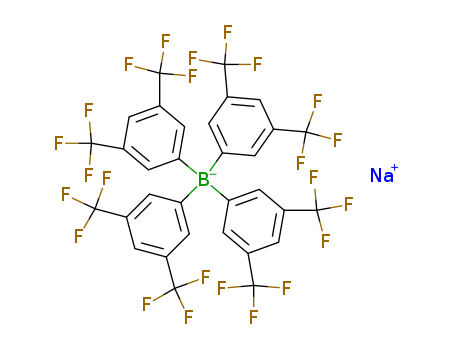
The study presents a novel palladium-catalyzed ligand-promoted alkynylation of aryl ketones. The protocol involves the conversion of aryl ketones into aryl electrophiles via Ar-C(O) cleavage, a challenging transformation in Sonogashira-type coupling. The key chemicals involved include aryl ketones as the starting materials, alkynylsilanes as the coupling partners, and a palladium catalyst along with a ligand, specifically a pyridine-oxazoline ligand (L32), which plays a crucial role in promoting the reaction. The reaction also utilizes potassium carbonate (K2CO3) as a base and sodium tetrakis[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]borate (NaBArF) as an additive. The process is carried out in a one-pot procedure, demonstrating broad functional-group tolerance and substrate scope. The study highlights the potential applications of this protocol in drug discovery and chemical biology by showcasing the late-stage diversification of pharmaceuticals and natural products. The method allows for the 1,2-bifunctionalization of aryl ketones, merging ketone-directed ortho-C-H activation with ligand-promoted ipso-Ar-C(O) alkynylation, providing a practical tool for the synthesis of biologically important molecules.


 Xn,
Xn, Xi
Xi


