Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 107-25-5 |
|---|---|
| Name: | Methyl vinyl ether |
| Article Data: | 67 |
| Molecular Structure: | |
|
|
|
| Formula: | C3H6O |
| Molecular Weight: | 58.08 |
| Synonyms: | Ether,methyl vinyl (8CI);1-Methoxyethylene;Methylvinyl ether;Vinyl methyl ether; |
| EINECS: | 203-475-4 |
| Density: | 0.73 g/ml |
| Melting Point: | -122.2oC |
| Boiling Point: | 5.5 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Appearance: | colorless gas |
| Hazard Symbols: |
 F+ F+
|
| Risk Codes: | 12 |
| Safety: | 9-16-33 |
| Transport Information: | UN 1087 |
| PSA: | 9.23000 |
| LogP: | 0.77630 |
- 144851-82-1METHYL2-AMINO-3-FLUOROBENZOATE
- 483366-12-7(2S,4R)-1-Boc-2-cyano-4-hydroxypyrrolidine
- 173606-50-3BOC-10-AMINODECANOIC ACID
- 361456-36-2METHYL (R)-(+)-ISOCYANATO-3-PHENYLPROPI&
- 5156-58-1N-(1-Benzyl-4-pipperidinyl)-N-phenylpropanamide HCl
- 81281-59-67-Benzylideneaminotheophylline
- 50288-62-5threo-Phenyl-2-piperidyl acetamide
- 82993-81-5D-threo-Ritalinic acid hydrochloride
- 47087-37-6Z-D-Glu-OMe
- 1219080-61-1IMIDAZOLE-2-BORONIC ACID

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With potassium hydroxide In dimethyl sulfoxide at 120℃; for 1h; Product distribution; other lower alcohols, other aprotic solvents; | 97% |
| With potassium hydroxide In dimethyl sulfoxide at 120℃; for 1h; | 97% |
| With potassium hydroxide at 150℃; under 14710.2 - 44130.5 Torr; |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With sodium In toluene Heating; | 76% |
- 111582-10-6
{(η5-Cp)iron(carbonyl)2CH2C(OMe)(carbonyl)2iron(η5-Cp)}(TfO)

A
- 107-25-5
methoxyethene

B
- 38117-54-3
cyclopentadienyl iron(II) dicarbonyl dimer

C
- 74171-11-2
(η5-Cp)iron(CO)2-α-methoxyethyl

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With methanol; sodium tetrahydroborate; sodium In methanol; dichloromethane Dissolving of Na and NaBH4 in MeOH, cooling (0°C), dropwise addn. of CH2Cl2 soln. of FpCH2C(OMe)FpTfO (Ar), stirring (5 min).; Methyl vinyl ether detd. by GlC, addn. of H2O, extn. (CH2Cl2), drying (MgSO4), column chromy. (Al2O3).; | A 54% B 41% C 27% |


| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With potassium hydroxide at 100℃; |
- 107-29-9Acetaldoxime
- 1073354-14-92-FORMYLPYRIDINE-5-BORONIC ACID PINACOLATE
- 1073-67-24-Chlorostyrene
- 1074-12-0PHENYLGLYOXAL
- 1074365-84-6Apixaban IMpurity 6
- 1074-40-42-Methoxy-4,6-dichloropyrimidine
- 107452-89-1Ziconotide acetate
- 107-45-9tert-Octylamine
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
Chemistry
Product Name: Methoxyethene (CAS NO.107-25-5)
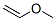
MF: C3H6O
MW: 58.08
EINECS: 203-475-4
Mol File: 107-25-5.mol
Surface Tension: 16.4 dyne/cm
Density: 0.73 g/ml
BP: 6°C
Index of Refraction: 1.357
Molar Refractivity: 17.41 cm3
Molar Volume: 79.5 cm3
Surface Tension:16.4 dyne/cm
Enthalpy of Vaporization: 24.36 kJ/mol
Vapour Pressure: 1500 mmHg at 25°C
XLogP3-AA: 0.8
H-Bond Donor: 0
H-Bond Acceptor: 1
Structure Descriptors of Methoxyethene (CAS NO.107-25-5):
IUPAC Name: methoxyethene
Canonical SMILES: COC=C
InChI: InChI=1S/C3H6O/c1-3-4-2/h3H,1H2,2H3
InChIKey: XJRBAMWJDBPFIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Uses
Methoxyethene (CAS NO.107-25-5) is used as the production of glutaraldehyde, and polymer materials, coatings, plasticizers, adhesives, etc.
Toxicity Data With Reference
| 1. | orl-rat LD50:4900 mg/kg | 34ZIAG Toxicology of Drugs and Chemicals ,Deichmann, W.B.,New York, NY.: Academic Press, Inc.,1969,395. | ||
| 2. | skn-rat LD50:>2 mL/kg | JACTDZ Journal of the American College of Toxicology. 12 (3)(1993),243. |
Consensus Reports
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by ingestion. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. Can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, stop flow of gas. Potentially explosive reaction with halogens (e.g., bromine, chlorine) or hydrogen halides (e.g., hydrogen bromide, hydrogen chloride). Reaction with acids forms acetaldehyde. Weak acids catalyze the exothermic polymerization of the ether. The unstabilized ether can form dangerous peroxides. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ETHERS and PEROXIDES, INORGANIC; PEROXIDES, ORGANIC.
Safety information of Methoxyethene (CAS NO.107-25-5):
Hazard Codes:  F+
F+
Risk Statements: 12
R12:Extremely Flammable ;
Safety Statements: 9-16-33
S9:Keep container in a well-ventilated place ;
S16:Keep away from sources of ignition - No smoking ;
S33:Take precautionary measures against static discharges ;
RIDADR: UN 1087
HazardClass: 2.1
Standards and Recommendations
DOT Classification: 2.1; Label: Flammable Gas
Specification
Methoxyethene , its CAS NO. is 107-25-5, the synonyms are 1-Methoxyethylene ; agrisynthmve ; Ethene,methoxy-;Ethenylmethylether ; ether,ethenylmethyl ; Ether, methyl vinyl . Methoxyethene (CAS NO.107-25-5) reacts vigorously with oxidizing materials. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat, flame or strong oxidizing agents. Reacts, possibly explosively with halogens (bromine, chlorine) or hydrogen halides (hydrogen bromide, hydrogen chloride) [Baker, 1980, p. 487]. On contact with dilute acids or even mildly acidic solids (calcium chloride, ceramics) undergoes rapid, exothermic homopolymerization, which cannot be prevented by antioxidants. Must be stored in the presence of base [MVE Brochure, Billingham, ICI, 1962].

