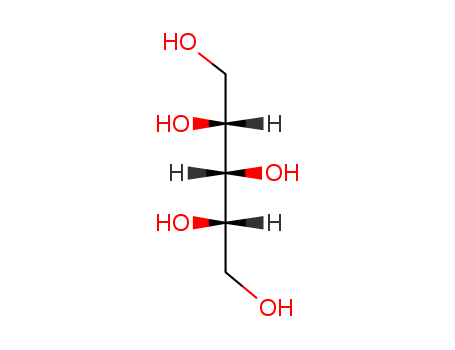
- Chemical Name:Pentitol
- CAS No.:87-99-0
- Deprecated CAS:12426-00-5,37191-59-6,7313-55-5,75398-81-1,84709-42-2
- Molecular Formula:C5H12O5
- Molecular Weight:152.147
- Hs Code.:29054910
- NSC Number:83253,25288,25283,16868
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID7042514
- Nikkaji Number:J1.453.993J
- Wikidata:Q81977867
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:123381
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL1369426
- Mol file:87-99-0.mol
Synonyms:(+--)-arabitol;arabinitol, D-;arabinitol, L-;arabino-pentitol;arabitol;arabitol, (D)-isomer;arabitol, (L)-isomer;D-arabinitol;D-arabitol;DL-arabitol;L-arabinitol;lyxitol


 Xi
Xi

