Inhibitors
Inhibitors refer to substances or compounds that selectively bind to and block the activity of specific enzymes, receptors, or other biological molecules. Their primary function is to regulate or inhibit biochemical processes within cells or organisms. Enzyme inhibitors, for example, can interfere with enzyme function by competitively or non-competitively binding to the enzyme's active site, thereby preventing substrate binding and subsequent catalysis. Receptor inhibitors act by binding to receptors on cell surfaces, blocking the binding of natural ligands or signaling molecules and thereby altering cellular responses.
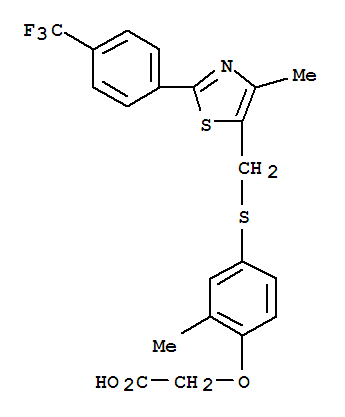
- Structure
- Product name
- CAS No.
- Molecular formula
- Inquiry
-
![(3S,3aR,4S,6S,6aR,7S,8S,9bS)-6-(acetyloxy)-4-(butanoyloxy)-3,3a-dihydroxy-3,6,9-trimethyl-8-{[(2Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoyl]oxy}-2-oxo-2,3,3a,4,5,6,6a,7,8,9b-decahydroazuleno[4,5-b]furan-7-yl octanoate](//file1.lookchem.com/300w/synthetic/2022-01-30-01/8b3fcf9d-a2c8-426d-8434-0b24bd4a9136.png)
-
(3S,3aR,4S,6S,6aR,7S,8S,9bS)-6-(acetyloxy)-4-(butanoyloxy)-3,3a-dihydroxy-3,6,9-trimethyl-8-{[(2Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoyl]oxy}-2-oxo-2,3,3a,4,5,6,6a,7,8,9b-decahydroazuleno[4,5-b]furan-7-yl octanoate
- 67526-95-8
- C34H50O12
- inquiry
Total:24 Page 1 of 1 1
![2-Fluoro-N-methyl-4-[7-[(quinolin-6-yl)methyl]imidazo[1,2-b]-[1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide Dihydrochloride](http://file1.lookchem.com/300w/substances/2022-02-23-02/d2ab18c3-ffef-4881-b3e7-3ce3c4bb6712.png)
![(1R)-6-fluoro-7-(2-fluoro-6-hydroxyphenyl)-1-[4-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-3-pyridinyl]-4-[(2S)-2-methyl-4-(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-1-piperazinyl]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2(1H)-one](http://file1.lookchem.com/300w/synthetic/2022-02-06-03/ee313aea-5c14-4300-815a-fb82e8994450.png)
![(3S,3aR,4S,6S,6aR,7S,8S,9bS)-6-(acetyloxy)-4-(butanoyloxy)-3,3a-dihydroxy-3,6,9-trimethyl-8-{[(2Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoyl]oxy}-2-oxo-2,3,3a,4,5,6,6a,7,8,9b-decahydroazuleno[4,5-b]furan-7-yl octanoate](http://file1.lookchem.com/300w/synthetic/2022-01-30-01/8b3fcf9d-a2c8-426d-8434-0b24bd4a9136.png)