
Journal of the American Chemical Society p. 8470 - 8479 (1989)
Update date:2022-08-11
Topics:
 Song, Byeong Doo
Song, Byeong Doo
 Jencks, William P.
Jencks, William P.
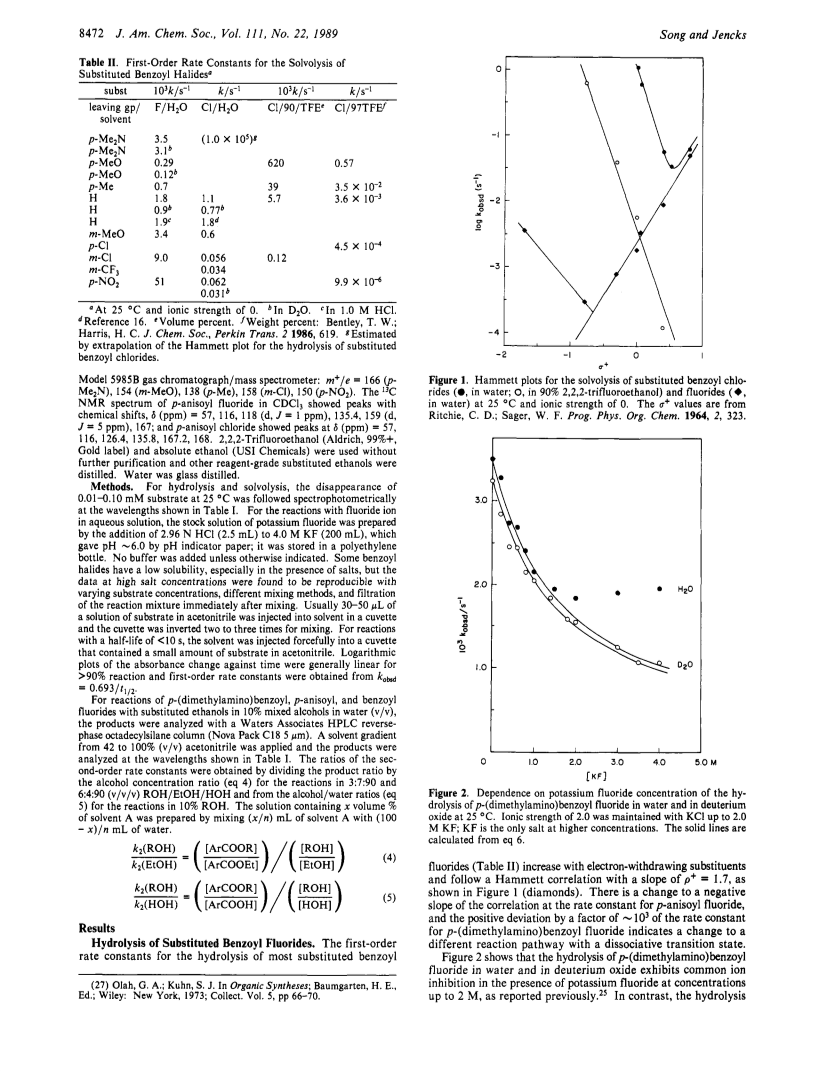
Most substituted benzoyl fluorides undergo hydrolysis in aqueous solution through an associative mechanism with ρ = 1.7, kHOH/kDOD = 2.3+/-0.2, little dependence on the leaving group (kCl/kF = 1.2), and general-base catalysis by fluoride ion.There is an abrupt change to a dissociative mechanism through an acylium ion intermediate for the hydrolysis of p-(dimethylamino)benzoyl and (in part) p-anisoyl fluorides, with ρ+ =/< -1.2, kCl/kF = 10E6-10E7, and kHOH/kDOD = 1.1 for p-Me2NPhCOF.Common ion inhibition by fluoride ion traps the p-(dimethylamino)benzoyl acylium ion, which undergoes hydration with kh ca. 10E9-10E10 s-1.The increase in the solvent isotope effect for hydrolysis of p-(dimethylamino)benzoyl fluoride to kHOH/kDOD = 1.9 in the presence of concentrated potassium fluoride is attributed to general-base-catalyzed hydration of the acylium ion intermediate.The large yield of trifluoroethyl ester from the solvolysis of p-anisoyl fluoride in TFE/EtOH/HOH suggests that the acylium ion reacts in a solvent-separated ion pair, with kh ca. 10E12 s-1; extrapolation predicts rate constants of =/> 10E13 s-1 for the hydration of less stable acylium ions.A change in sensitivity to solvent ionizing power from m = 1.4 in water to m = 0 in 60percent ethanol for p-(dimethylamino)benzoyl fluoride suggests a change to an associative mechanism.Benzoyl fluorides and acylium ions show selectivity toward alcohols, with βnuc ca. 0.2.The absence of common ion inhibition for the solvolysis of several benzoyl chlorides in water or 90percent TFE/HOH is consistent with kh >10E11 s-1 for the acylium ions.Solvolysis occurs through the dissociative reaction channel, with ρ+ = -3.0, even when the estimated lifetimes of the acylium ion species suggest that there is no chemical barrier for their hydration.However, there is a change to an associative mechanism for the solvolysis of p-nitrobenzoyl chloride in water.
View More








Changzhou Sunlight Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Contact:+86-519-83131668;83139028;83138042;83137041
Address:JiuliStreet, Benniu Town Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province
Contact:0086-29-89196322
Address:North of the Fifth Keji Road, Hi-Tech Industrial Zone, Xi'an City, Shaanxi Province, China
FREEBARQUE DEVELOPMENT GROUP LIMITED
Contact:+86(0)10-5109 5335 or 5109 5345
Address:Room602,Block1-B,LINGDI OFFICE,NO.13 BEIYUAN ROAD
QINGDAO ON-BILLION INDUSTRAIL CO.,LTD
website:http://www.obn.com.cn
Contact:+86-15005320811 +86-532-80681989
Address:F35 Parkson Mansion No.44-60 Zhongshan Rd.
Jinan Jianfeng Chemical Co., Ltd
Contact:0086-531-88110457
Address:sales01(-a-t-)pharmachemm{dot}c+o+m
Doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)98826-X
(1984)Doi:10.1039/c6ra15483b
(2016)Doi:10.1590/S0103-50532012000300025
(2012)Doi:10.1039/ft9918701265
(1991)Doi:10.1021/jo01067a036
(1961)Doi:10.1007/s10895-015-1691-1
(2016)