10.1002/jccs.201300586
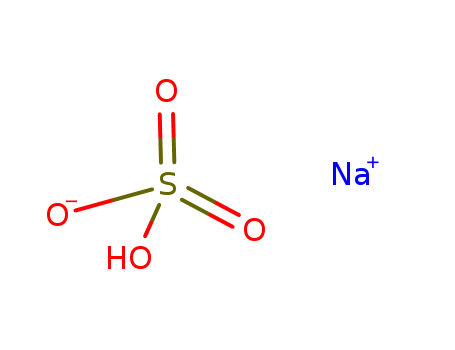
The research focuses on the preparation and application of nano silica supported sodium hydrogen sulfate (NaHSO4.SiO2 (nano)) as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of silyl ethers from various alcohols and phenols under both solution and solvent-free conditions. The study introduces a new method using chlorosilanes instead of hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS), aiming to overcome drawbacks such as long reaction times, harsh conditions, and the use of toxic or expensive reagents associated with traditional silylation methods. The experiments involved the preparation of silyl ethers using NaHSO4.SiO2 (nano) and triethylamine (Et3N) with chlorosilanes as silylating agents. The reactants included a range of alcohols and phenols, which were subjected to trimethyl, triethyl, and t-butyldimethyl silylations. The analyses used to characterize the synthesized silyl ethers included physical constants, infrared (IR) spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and mass spectroscopy. The study demonstrated that the new method could achieve high yields of silyl ethers in relatively short reaction times under mild conditions, with the added benefit of avoiding the need for solvents, thus simplifying the work-up procedure.


 Xi
Xi


