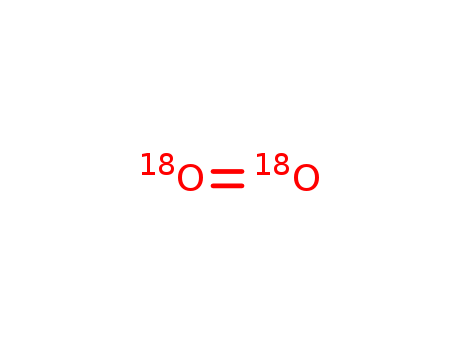- Chemical Name:Oxygen-18O2
- CAS No.:32767-18-3
- Molecular Formula:O2
- Molecular Weight:38.0159
- Hs Code.:
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID80437936
- Wikidata:Q82253542
- Mol file:32767-18-3.mol
Synonyms:Oxygen-18O2;32767-18-3;DTXSID80437936;Oxygen-18O2, 90 atom % 18O;Oxygen-18O2, 97 atom % 18O;18O2;Oxygen-18O2, 10 atom % 18O (random);Oxygen-18O2, 25 atom % 18O (random);Oxygen-18O2, 50 atom % 18O (random);Oxygen-18O2, 99 atom % 18O, 99% (CP);Oxygen-18O2, 97 atom % 18O, 99.99% (CP)