Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 99-04-7 |
|---|---|
| Name: | m-Toluic acid |
| Article Data: | 350 |
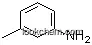
| Molecular Structure: | |
|
|
|
| Formula: | C8H8O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 136.15 |
| Synonyms: | 3-methylbenzoate; zinc(+2) cation;Benzoic acid, 3-methyl-, cadmium salt;beta-Bethylbenzoic acid;Zinc 3-methylbenzoate;m-Methylbenzoate;Barium 3-methylbenzoate;Benzoic acid, 3-methyl-;m-Methylbenzoic acid;Cadmium 3-methylbenzoate;Benzoic acid, 3-methyl-, barium salt;beta-Methylbenzoic acid;Barium m-toluate;3-methylbenzoate;3-methylbenzoic acid;Zinc m-toluate;1/C8H8O2/c1-6-3-2-4-7(5-6)8(9)10/h2-5H,1H3,(H,9,10;cadmium(+2) cation; 3-methylbenzoate;Benzoic acid, 3-methyl-, zinc salt;Cadmium m-toluate;m-Toluicacid; |
| EINECS: | 202-723-9 |
| Density: | 1.151 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point: | 108 °C |
| Boiling Point: | 263.8 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point: | 120 °C |
| Solubility: | water: 1.054 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Appearance: | off-white crystalline solid |
| Hazard Symbols: |
 Xn Xn
|
| Risk Codes: | 22 |
| Safety: | 22-24/25-36 |
| PSA: | 37.30000 |
| LogP: | 1.69320 |
- 99170-93-1N-Methyl-2-oxazolamine
- 99724-17-1Dimethyl-pyrrolidin-3-ylmethyl-amine
- 99421-19-9ethyl 3-amino-6-chloro-5-cyano-2-methylisonicotinate
- 99689-20-02-Acetamido-3-O-(D-1-carboxyethyl)-2-deoxy-2-D-glucose Methyl Ester
- 99183-99-04-Chloro-7-methoxy-1-indanone, 97%
- 99070-23-24-(2-bromoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzaldehyde
- 99662-46-1triphenyl(2-pyridylmethyl)phosphonium chloride hy
- 99735-47-4((R)-1-((R)-1-phenylethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)methanol
- 99735-45-2(R)-methyl 5-oxo-1-((R)-1-phenylethyl)pyrrolidine-3-carboxylate
- 99533-99-03'-MERCAPTOACETAMINOPHEN

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With 2-mesityl-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazol-2-ium tetrafluoroborate; 1,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-2H-pyrimido[1,2-a]pyrimidine In acetonitrile at 20℃; | 99% |
| With tert.-butylhydroperoxide; water; iodine; sodium hydroxide at 70℃; pH=10; Green chemistry; | 95% |
| With 2-mesityl-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,2,4]triazol-2-ium tetrafluoroborate; 1,4-diaza-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane; oxygen In tetrahydrofuran at 20℃; for 16h; | 95% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With amphiphilic resin-supported phosphine-palladium; water; potassium carbonate at 25℃; under 760 Torr; hydroxycarbonylation; | 99% |
| With water; potassium carbonate In acetonitrile at 100℃; under 3750.38 Torr; for 0.0161111h; | 98% |
| With 4,4’‐bis(trimethylammoniummethyl)‐2,2’‐bipyridine; bis-triphenylphosphine-palladium(II) chloride; water; sodium carbonate In water at 100℃; under 7600.51 Torr; for 24h; Catalytic behavior; Autoclave; | 86% |
| With water; palladium diacetate; triethylamine; 4,5-bis(diphenylphos4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthenephino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene In 1,4-dioxane at 100℃; under 11251.1 Torr; Flow reactor; | 58% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With water; sodium hydroxide at 100℃; for 4h; Temperature; | 98.5% |
| With hydrogenchloride im Druckrohr; | |
| With steam; thorium dioxide at 420℃; | |
| With sulfuric acid | |
| With nitrilase from Gordonia terrae In aq. phosphate buffer at 35℃; for 1h; pH=8; Enzymatic reaction; |
- 61560-94-9
3-methylphenyloxoacetic acid

- 99-04-7
m-Toluic acid

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With oxone In N,N-dimethyl-formamide for 4h; | 98% |
- 73318-83-9
2-oxo-2-(m-tolyl)acetaldehyde

- 99-04-7
m-Toluic acid

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With oxone In N,N-dimethyl-formamide for 4h; | 98% |
| With tert.-butylhydroperoxide for 7h; | 82% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With diethylene glycol dimethyl ether at 70℃; for 0.5h; Sonication; | 97% |
| With oxygen; sodium hydroxide In water at 80℃; for 10h; Catalytic behavior; | 97% |
| With tert.-butylhydroperoxide; water; iodine; sodium hydroxide at 70℃; pH=10; Green chemistry; | 90% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With potassium hydroxide; palladium dichloride In water at 100℃; for 5h; Condensation; | 97% |
- 136125-68-3
methyl 3-methylphenylglyoxylate

- 99-04-7
m-Toluic acid

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With oxone In N,N-dimethyl-formamide for 4h; | 97% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With dihydrogen peroxide In dimethyl sulfoxide at 70℃; for 10h; Catalytic behavior; Reagent/catalyst; Overall yield = > 99 %; | A 96% B n/a C n/a |
| With cobalt(II) acetate; manganese(II) acetate; acetic acid; 3-benzyl-1-methylimidazolium bromide at 215℃; for 3h; |

- 53663-39-1
3-methyl-2-bromobenzoic acid

- 99-04-7
m-Toluic acid

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With isopropyl alcohol for 5h; Schlenk technique; Inert atmosphere; Irradiation; Heating; | 96% |
| With [RhCl2(p-cymene)]2; cesium acetate In isopropyl alcohol at 20 - 100℃; for 24h; Inert atmosphere; | 94% |
| With [ruthenium(II)(η6-1-methyl-4-isopropyl-benzene)(chloride)(μ-chloride)]2; cesium acetate; isopropyl alcohol at 100℃; Schlenk technique; Inert atmosphere; | 93% |
- 113170-55-1Magnesium ascorbyl phosphate
- 1575-61-7Pentanoylchloride, 5-chloro-
- 142-63-2Piperazine, hydrate (1:6)
- 102-09-0Diphenyl carbonate
- 386750-22-7Desvenlafaxine succinate
- 5025-82-14-Thiazolidinecarboxylic acid, 3-acetyl-
- 91-44-12H-1-Benzopyran-2-one,7-(diethylamino)-4-methyl-
- 12126-59-9ConjugatedEstrogens
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
Chemistry
IUPAC Name: 3-Methylbenzoic acid
Synonyms: 3-Methylbenzoic acid ; Benzoic acid, 3-methyl- ; 3-Methyl-Benzoic Acid ; 3-Toluic acid
Product Categories: Aromatic Carboxylic Acids, Amides, Anilides, Anhydrides & Salts;Organic acids
Molecular Structure of M-toluic acid (CAS NO.99-04-7) : 
Molecular Formula of M-toluic acid (CAS NO.99-04-7) : C8H8O2
Molecular Weight of M-toluic acid (CAS NO.99-04-7) : 136.15
CAS NO: 99-04-7
EINECS: 202-723-9
Index of Refraction: 1.556
Surface Tension: 45.4 dyne/cm
Density: 1.151 g/cm3
Flash Point: 120 °C
Enthalpy of Vaporization: 53 kJ/mol
Boiling Point: 263.8 °C at 760 mmHg
Vapour Pressure: 0.00506 mmHg at 25°C
Melting point: 108 °C
Water Solubility : <0.1 g/100 mL at 19 ºC
Stability: Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents
General Description :White to yellowish crystals or mostly yellow flaky solid (with some white flakes). Has a floral-honey odor.
Uses
It serves, among other purposes, as a precursor to DEET (N,N diethyl-m-toluamide) the well-known insect repellent.

Production
Preparation Products: 3-Carboxybenzaldehyde-->3-(4-Methylpiperazin-1-ylmethyl)benzoic acid-->Methyl 3-(morpholinomethyl)benzoate ,98%-->METHYL 3-((PYRROLIDIN-1-YL)METHYL)BENZOATE-->3-(BROMOMETHYL)BENZOIC ACID-->3-BENZOYLPHENYLACETIC ACID-->3-Methylbenzophenone-->N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide
Raw materials :m-Xylene-->1,3-Bisbenzyl-2-oxoimidazolidine-4,5-dicarboxylic acid
M-toluic acid (CAS NO.99-04-7) is derived from m-Xylene catalytic oxidation. cobalt naphthenate as a catalyst , m-Xylene oxidation by using air , the reaction temperature is 125-135 °C, pressure is about 0.25MPa. Per ton of product consumption of 1700kg m-Xylene.
Toxicity Data With Reference
| Organism | Test Type | Route | Reported Dose (Normalized Dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 562mg/kg (562mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: REGIDITY BEHAVIORAL: MUSCLE CONTRACTION OR SPASTICITY) | Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 11, Pg. 1020, 1968. |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 1630mg/kg (1630mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: MUSCLE WEAKNESS LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING | Gigiena Truda i Professional'nye Zabolevaniya. Labor Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. Vol. 18(7), Pg. 57, 1974. |
| rat | LD | oral | > 5gm/kg (5000mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: EXCITEMENT GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING | Gigiena Truda i Professional'nye Zabolevaniya. Labor Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. Vol. 18(7), Pg. 57, 1974. |
Safety Profile
Hazard Codes  Xn
Xn
Risk Statements 22
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
Safety Statements 22-24/25-36
S22:Do not breathe dust.
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing.
WGK Germany 3
RTECS XU1200000
HS Code 29163900
Specification
1.Air & Water Reactions :Fine dust dispensed in air in sufficient concentrations, and in the presence of an ignition source is a potential dust explosion hazard. . Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile m-Toluic acid is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in m-Toluic acid to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions. m-Toluic acid is incompatible with strong oxidizers.
2.Fire Hazard Flash point data for m-Toluic acid are not available; however, m-Toluic acid is probably combustible.