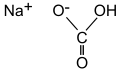
- Chemical Name:Sodium bicarbonate
- CAS No.:144-55-8
- Molecular Formula:NaHCO3
- Molecular Weight:84.0069
- Hs Code.:28363000
- Mol file:144-55-8.mol
Synonyms:Carbonic acid, monosodium salt;Natriumhydrogenkarbonat;Meylon;Carbonic acid disodium salt;SodaSee;Monosodium hydrogen carbonate;Monosodium carbonate;monosodium salt ;; see the subdivided heading;Component of Col-Evac;Soda Mint;Sodium bicarbonate(1:1);Carbonic acid, disodium salt;Natriumbicarbonat, Natriumhydrogencarbonat;Sodium Bicarbonate food grade;