Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 3282-30-2 |
|---|---|
| Name: | Pivaloyl chloride |
| Article Data: | 132 |
| Molecular Structure: | |
|
|
|
| Formula: | C5H9ClO |
| Molecular Weight: | 120.579 |
| Synonyms: | Propanoyl chloride,2,2-dimethyl-;Trimethylacetyl chloride [UN2438] [Poison];Trimethylacetyl chloride;Propanoyl chloride, 2,2-dimethyl-;Trimethylacetychloride; |
| EINECS: | 221-921-6 |
| Density: | 1.008 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point: | -56 °C |
| Boiling Point: | 107.2 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point: | 8.9 °C |
| Solubility: | hydrolysis with water |
| Appearance: | colorless to yellow liquid |
| Hazard Symbols: |
 F, F,  T+, T+,  T T
|
| Risk Codes: | 11-14-22-26-34-23 |
| Safety: | 16-26-36/37/39-45-38-28A |
| Transport Information: | UN 2438 6.1/PG 1 |
| PSA: | 17.07000 |
| LogP: | 1.79790 |
- 483366-12-7(2S,4R)-1-Boc-2-cyano-4-hydroxypyrrolidine
- 361456-36-2METHYL (R)-(+)-ISOCYANATO-3-PHENYLPROPI&
- 5156-58-1N-(1-Benzyl-4-pipperidinyl)-N-phenylpropanamide HCl
- 81281-59-67-Benzylideneaminotheophylline
- 50288-62-5threo-Phenyl-2-piperidyl acetamide
- 82993-81-5D-threo-Ritalinic acid hydrochloride
- 47087-37-6Z-D-Glu-OMe
- 73441-42-6METHYL-5-CHLORO-2,2-DIMETHYLVALERATE
- 68439-39-4Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha-(2-ethylhexyl)-omega-hydroxy-,
- 852475-26-4MC1568
- 1634-04-4
tert-butyl methyl ether

- 106-47-8
4-chloro-aniline

A
- 65854-91-3
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,2-dimethylpropionamide

B
- 3282-30-2
pivaloyl chloride

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With sodium hydroxide In water | A 97% B n/a |
| With sodium hydroxide In water | A 97% B n/a |
| With sodium hydroxide In water | A 97% B n/a |
| With sodium hydroxide In water | A 97% B n/a |


| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With benzoyl chloride | 88% |
| With tetrachlorosilane at 50 - 55℃; for 5h; | 72% |
| With thionyl chloride for 24h; Ambient temperature; | 29% |
- 78114-26-8, 114091-61-1, 63853-15-6
(2,2-dimethyl-1-(trimethylsiloxy)propylidene)-trimethylsilylphosphine

A
- 3282-30-2
pivaloyl chloride

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With sulfuryl dichloride | A 81% B n/a |
- 124-63-0
methanesulfonyl chloride

- 75-98-9
Trimethylacetic acid

A
- 3282-30-2
pivaloyl chloride

B
- 1538-75-6
2,2-dimethylpropanoic anhydride

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With triethylamine In dichloromethane at 0℃; | A 54% B 5% C 35% |


| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With methanesulfonyl chloride; triethylamine In dichloromethane at 0℃; | A 54% B 5% C 35% |


| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With trifluorormethanesulfonic acid In trichlorofluoromethane at -45℃; under 37503 Torr; for 1h; Product distribution; | 50% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With trifluorormethanesulfonic acid In trichlorofluoromethane at -45℃; under 37503 Torr; for 1h; | 50% |
- 507-20-0
tertiary butyl chloride

A
- 14705-30-7
2,2,5-trimethyl-hex-4-en-3-one

B
- 36967-88-1
Pivalinsaeure-trifluormethansulfonsaeure-anhydrid

C
- 3282-30-2
pivaloyl chloride

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With trifluorormethanesulfonic acid In tetrachloromethane at -25℃; under 56254.5 Torr; for 1h; | A n/a B n/a C 47% D n/a |

- 507-20-0
tertiary butyl chloride

- 1493-13-6
trifluorormethanesulfonic acid

A
- 14705-30-7
2,2,5-trimethyl-hex-4-en-3-one

B
- 36967-88-1
Pivalinsaeure-trifluormethansulfonsaeure-anhydrid

C
- 3282-30-2
pivaloyl chloride

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| In tetrachloromethane at -25℃; under 56254.5 Torr; for 1h; | A n/a B n/a C 47% |

- 18243-80-6
trichloro-pivaloyloxy-silane

- 3282-30-2
pivaloyl chloride

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| at 159 - 161℃; |
- 532-43-4Thiamine nitrate
- 10279-57-9Silica hydrate
- 122-39-4Diphenylamine
- 100643-71-8Desloratadine
- 98-56-64-Chlorobenzotrifluoride
- 109-70-61-Bromo-3-chloropropane
- 9001-73-4Papain
- 372-18-91,3-Difluorobenzene
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
Chemistry
Molecule structure of Pivaloyl chloride (CAS NO.3282-30-2):
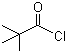
IUPAC Name: 2,2-Dimethylpropanoyl chloride
Molecular Weight: 120.57736 g/mol
Molecular Formula: C5H9ClO
Density: 1.008 g/cm3
Melting Point: -56 °C
Boiling Point: 107.2 °C at 760 mmHg
Flash Point: 8.9 °C
Index of Refraction: 1.416
Molar Refractivity: 30.05 cm3
Molar Volume: 119.6 cm3
Surface Tension: 25.8 dyne/cm
Enthalpy of Vaporization: 34.6 kJ/mol
Vapour Pressure: 27.4 mmHg at 25 °C
Storage Temp.: store at RT.
Water Solubility: hydrolysis
Sensitive: moisture sensitive
XLogP3-AA: 2.2
H-Bond Acceptor: 1
Rotatable Bond Count: 1
Exact Mass: 120.034193
MonoIsotopic Mass: 120.034193
Topological Polar Surface Area: 17.1
Heavy Atom Count: 7
Canonical SMILES: CC(C)(C)C(=O)Cl
InChI: InChI=1S/C5H9ClO/c1-5(2,3)4(6)7/h1-3H3
InChIKey: JVSFQJZRHXAUGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
EINECS: 221-921-6
Uses
Pivaloyl chloride (CAS NO.3282-30-2) is used as acylating agent for the production of drugs such as ampicillin and cephalexin. It is also used for medicine and pesticide intermediates.
Consensus Reports
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory.
Safety Profile
Hazard Codes:  F,
F,  T+,
T+,  T
T
Risk Statements: 11-14-22-26-34-23
R11:Highly flammable.
R14 :Reacts violently with water.
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R26:Very toxic by inhalation.
R34:Causes burns.
R23 :Toxic by inhalation.
Safety Statements: 16-26-36/37/39-45-38-28A
S16:Keep away from sources of ignition.
S26: In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection.
S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.)
S38:In case of insufficient ventilation, wear suitable respiratory equipment.
S28:After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of soap-suds.
RIDADR: UN 2438 6.1/PG 1
WGK Germany: 1
F: 9-19
HazardClass: 6.1
PackingGroup: I
HS Code: 29159080
A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. The liquid is flammable when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl−.
Standards and Recommendations
DOT Classification: 8; Label: Corrosive, Flammable Liquid, Poison
Specification
Pivaloyl chloride (CAS NO.3282-30-2) is also named as 2,2-Dimethylpropanoyl chloride ; Propanoyl chloride, 2,2-dimethyl- ; Trimethylacetyl chloride ; UN2438 . Pivaloyl chloride (CAS NO.3282-30-2) is colorless to yellow liquid with a pungent odor. It is very toxic by inhalation, ingestion or skin absorption. Fumes irritate the eyes and mucous membranes. Corrosive to most metals and tissue. It is highly flammable. Reacts vigorously and exothermically with water to form trimethylacetic acid and corrosive hydrochloric acid; both acids corrode metals and tissue. Pivaloyl chloride is acidic and incompatible with bases (including amines), strong oxidizing agents, and alcohols. May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts. May cause toxic effects if inhaled or ingested/swallowed. Contact with substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated.

