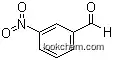
99-61-6Relevant articles and documents
Acid-Catalyzed Photooxidation of m-Nitrobenzyl Derivatives ib Aqueous Solution
Rafizadeh, Karim,Yates, Keith
, p. 2777 - 2781 (1986)
A variety of m-nitrobenzyl derivatives including alcohols, alkyl ethers, esters, and an amine undergo photooxidation reactions to produce m-nitrobenzaldehyde (or m-nitroacetophenone in two cases) as the major isolated product.The reaction is both solvent and pH dependent and only takes place in essentially aqueous media.The quantum efficiency of product formation reaches a maximum (φ =0.3-0.4) in the 20-50percent sulfuric acid range, depending on the substrate, although the reaction is reasonably efficient even in neutral aqueous solution.The presence of benzylic hydrogen and a heteroatom (O,N) in the α-position appears to be essential for photooxidation to occur.The multiplicity of the reactive state is T1.A solvent isotope effect (φH2O/φD2O = 1.4) was observed.The proposed mechanism involves rate-determining protonation of T1 followed by rapid α-hydrogen abstraction by water.
A facile method for the transformation of acetals and ketals to aldehydes and ketones
Wu,Ding
, p. 2173 - 2177 (1994)
This paper reports a simple and convenient acetyl chloride-samarium trichloride system for the transformation of acetals and ketals to aldehydes and ketones.
Selective oxidation of benzylic alcohols using can supported onto silica gel under microwave irradiation
Heravi, Majid M.,Oskooie, Hossein A.,Kazemian, Pegah,Drikvand, Fatemeh,Ghassemzadeh, Mitra
, p. 2341 - 2344 (2004)
Cerium ammonium nitrate (CAN) adsorbed on HNO3/silica gel is a mild reagent for selective oxidation of benzylic alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes under microwave irradiation in solventless system.
Zinc Photocages with Improved Photophysical Properties and Cell Permeability Imparted by Ternary Complex Formation
Basa, Prem N.,Barr, Chelsea A.,Oakley, Kady M.,Liang, Xiaomeng,Burdette, Shawn C.
, p. 12100 - 12108 (2019)
Photocaged complexes can control the availability of metal ions to interrogate cellular signaling pathways. We describe a new photocage, {bis[(2-pyridyl)methyl]amino}(9-oxo-2-xanthenyl)acetic acid (XDPAdeCage, 1), which utilizes a 2-xanthone acetic acid group to mediate a photodecarboxylation reaction. XDPAdeCage photolyzes with a quantum yield of 27%, and binds Zn2+ with 4.6 pM affinity, which decreases by over 4 orders of magnitude after photolysis. For comparison to our previous approach to Zn2+ release via photodecarboxylation, the analogous photocage {bis[(2-pyridyl)methyl]amino}(m-nitrophenyl)acetic acid (DPAdeCage, 2), which uses a m-nitrobenzyl chromophore, was also prepared and characterized. The advantages of the 2-xanthone acetic acid chromophore include red-shifted excitation and a higher extinction coefficient at the preferred uncaging wavelength. The neutral ternary complex of [Zn(XDPAdeCage)]+ with the anionic ligand pyrithione is membrane permeable, which circumvents the need to utilize invasive techniques to introduce intracellular Zn2+ fluctuations. Using fluorescent imaging, we have confirmed transport of Zn2+ across membranes; in addition, RT-PCR experiments demonstrate changes in expression of Zn2+-responsive proteins after photolysis.
Controlled reduction of activated primary and secondary amides into aldehydes with diisobutylaluminum hydride
Azeez, Sadaf,Kandasamy, Jeyakumar,Sabiah, Shahulhameed,Sureshbabu, Popuri
supporting information, p. 2048 - 2053 (2022/03/31)
A practical method is disclosed for the reduction of activated primary and secondary amides into aldehydes using diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBAL-H) in toluene. A wide range of aryl and alkyl N-Boc, N,N-diBoc and N-tosyl amides were converted into the corresponding aldehydes in good to excellent yields. Reduction susceptible functional groups such as nitro, cyano, alkene and alkyne groups were found to be stable. Broad substrate scope, functional group compatibility and quick conversions are the salient features of this methodology.
Trifunctional covalent triazine and carbonyl based polymer as a catalyst for one-pot multistep organic transformation
Ravi, Seenu,Raza, A. Ahmed,Sheriff, A. K. Ibrahim,Tajudeen, S. Syed
, (2021/08/24)
Trifunctional covalent triazine and carbonyl based polymer with acid-base and metal active sites (CTCP-SO3H-EDA/Pd) was synthesized by a multistep friedel-crafts reaction, post-synthetic sulfonation, schiff base condensation and metal nanoparticle incorporation. CTCP-SO3H-EDA/Pd was characterized by FT-IR, N2 sorption-desorption isotherm, elemental analysis, ICP-OES, TEM-EDS and TEM. CTCP-SO3H-EDA/Pd was evaluated as a heterogeneous catalyst for the conversion of 1-(dimethoxymethyl)-3-nitrobenzene into 2-(3-aminobenzylidene)malononitrile via a three step deacetylation-Knoevenagel and transfer hydrogenation reaction in one domino process. The cooperation of SO3H acidic sites, EDA and uniformly distributed Pd nanoparticles greatly facilitated the one-pot reaction and produced good yield of the desired product with high selectivity. The catalyst was recovered by simple centrifugation and could be reused for five runs with minor loss of catalytic activity and selectivity. A plausible mechanism for deacetylation, C[sbnd]C bond formation and subsequent chemoselective reduction of nitro functionality over CTCP-SO3H-EDA/Pd was also proposed.
The: In situ fabrication of ZIF-67 on titania-coated magnetic nanoparticles: A new platform for the immobilization of Pd(ii) with enhanced catalytic activity for organic transformations
Kaur, Manpreet,Paul, Satya,Sharma, Chandan,Sharma, Sukanya
, p. 20309 - 20322 (2021/11/22)
Considering the outstanding characteristics of metal organic frameworks (MOFs) and magnetic nanoparticles, herein we report a facile approach for the synthesis of a magnetic zeolitic-imidazolate-framework-supported palladium(ii) catalyst. In brief, zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67) was successfully incorporated onto the surface of titania-coated magnetic nanoparticles using ethane-1,2-diamine as a linker, and then Pd(ii) was immobilized onto this. The resulting Pd@ZIF-67-Fe3O4-TiO2 catalyst possesses a high surface area (205 m2 g-1), a large pore volume (0.10 cm3 g-1), good magnetic responsivity (10.71 emu g-1), and high stability. A comparative analysis of Pd@ZIF-67-Fe3O4-TiO2 and Pd@Fe3O4-TiO2 catalysts for the oxidation, reduction, and oxidative deprotection of oximes was done to investigate the effects of ZIF-67 on the catalytic performance of Pd species. Substantial differences in activity and stability were observed in the presence of ZIF-67, suggesting that ZIF-67 plays an important role in enhancing the activity of Pd(ii). This superior catalytic activity and stability arises due to a synergistic effect between well-dispersed palladium species and highly porous ZIF-67, which was confirmed via XPS analysis. Moreover, the catalyst retains its structure, chemical environment, and good magnetic response even after five catalytic runs, as confirmed via FTIR, XRD, XPS, and VSM studies of reused catalyst samples.
Efficient strategy for interchangeable roles in a green and sustainable redox catalytic system: IL/PdII-decorated SBA-15 as a mesoporous nanocatalyst
Sadeghi, Samira,Karimi, Meghdad,Radfar, Iman,Gavinehroudi, Reza Ghahremani,Saberi, Dariush,Heydari, Akbar
, p. 6682 - 6692 (2021/04/22)
Time and again, SBA-15-based composites as mesoporous materials and the incorporation of transition metals in them have been attracting dramatic attention in the field of catalysis due to their remarkable features. In this paper, the activity of SBA-15 supported ionic liquid-Pd(ii) has been investigated in the catalytic transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes with formic acid as a hydrogen donor at room temperature in water medium, and the oxidation of benzyl alcohols to benzaldehyde derivatives under atmospheric oxygen at high temperature. This novel nanocatalyst was characterized by FT-IR, SA-XRD, BET, BJH, TGA, FE-SEM, TEM, and ICP as the most commonplace techniques for analyzing its characteristics to be revealed as truth. Furthermore, the EDX analysis illustrates the grafting of the ionic liquid-Pd(ii) into SBA-15. The catalyst showed high stability under reaction conditions, and can be recovered and reused for at least 15 and 6 reaction runs in oxidation and reduction reactions, respectively.
Magneto-structural properties and reliability of (Mn/Ni/Zn) substituted cobalt-copper ferrite heterogeneous catalyst for selective and efficient oxidation of aryl alcohols
Dhabbe, Rohant,Gaikwad, Pratapsingh,Kakade, Bhalchandra,Kamble, Prakash,Kurane, Rajnikant,Parase, Haridas,Sabale, Sandip
, (2021/09/28)
Herein, M2+ substituted CoCuFe2O4 (M2+ = Mn, Zn, Ni) ferrites have been synthesized using the sol-gel auto combustion method. The structural, morphological and magnetic studies confirm the phase formation of pure magnetic cubic spinel MCoCuFe2O4 (M2+ = Mn, Zn, Ni) ferrites. The substitution with Mn, Ni and Zn does not show large variation in binding energies obtained from XPS of Cu (2p) that specifies identical copper concentration (Cu0.5) and substitution of only cobalt (Co2+) in Mn-F, Ni-F and Zn-F catalysts. Interestingly, MCoCuFe2O4 magnetic catalysts were explored for selective oxidation of a series of substituted benzyl alcohols. Catalyst Mn-F showed 93% conversion of benzyl alcohol while, Ni-F showed 95% conversion of 4-nitrobenzyl alcohol. Whereas, the catalyst Zn-F was showed 96% conversion for 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol. Additionally the results also indicate an efficient separation and recovery of the magnetic catalysts after four successive reuses without any considerable loss in its catalytic activity.
A novel two-dimensional metal-organic framework as a recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for the dehydrogenative oxidation of alcohol and theN-arylation of azole compounds
Liu, Chengxin,Cui, Jin,Wang, Yufang,Zhang, Mingjie
, p. 11739 - 11744 (2021/03/31)
A novel metal-organic framework (MOF) with two-dimensional (2D) crystal structure was developed using Cu(NO3)2·3H2O and 2,2′,5,5′-tetramethoxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid. Further, its structure was characterized using infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetry, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray crystallography. The activated Cu-MOF was used to catalyze the dehydrogenative oxidation of alcohol andN-arylation of azole compounds. Furthermore, it could be easily recovered and reused.