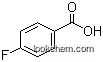
456-22-4Relevant articles and documents
Platinum nanoparticles supported on polymeric ionic liquid functionalized magnetic silica: effective and reusable heterogeneous catalysts for the selective oxidation of alcohols in water
Vessally, Esmail,Ghasemisarabbadeih, Mostafa,Ekhteyari, Zeynab,Hosseinzadeh-Khanmiri, Rahim,Ghorbani-Kalhor, Ebrahim,Ejlali, Ladan
, p. 106769 - 106777 (2016)
In this research, the syntheses of core-shell magnetic silica nanostructures, functionalized by a polymeric ionic liquid and immobilization of platinum nanoparticles, are described. Firstly, the magnetic silica nanoparticles were synthesized and modified using an amine-containing organosilane through a single-step process. The synthesized nanostructures were functionalized by the synthesis and polymerization of a pyridinium ionic liquid and a methyl methacrylate monomer, respectively, onto their surfaces. The platinum nanoparticles were immobilized on the functionalized nanoparticles. The obtained functionalized nanostructures have been used in the selective aerobic oxidation, in an aqueous medium, of primary and encumbered secondary aliphatic alcohols, and exhibit high activity at mild temperatures.
Role of water and p-fluorobenzoic acid in mn(ii)t(p-cl)pp catalyzed aerobic oxidation of p-fluorotoluene
Fang, Yong-Qi,Lv, Chun-Xu,Lu, Ming
, p. 313 - 315 (2013)
A solvent-free manganoporphyrin-catalyzed oxidiation of p-fluorotoluene was developed, using oxygen as a clean and cheap oxidant. The parameters that have relationship with conversion were investigated. The conversion of p-fluorotoluene was found to be depend on the stability of catalytic environment. Water and p-fluorobenzoic acid were the final oxidation products of p-fluorotoluene, would inhibit the activity of catalyst. The conversion would be increased from 7.0 to 16.5 %, by the dehydration of acetic anhydride.
New benzothiazole based copper(II) hydrazone Schiff base complexes for selective and environmentally friendly oxidation of benzylic alcohols: The importance of the bimetallic species tuned by the choice of the counterion
Bocian, Aleksandra,Gorczyński, Adam,Marcinkowski, Damian,Witomska, Samanta,Kubicki, Maciej,Mech, Paulina,Bogunia, Ma?gorzata,Brzeski, Jakub,Makowski, Mariusz,Pawlu?, Piotr,Patroniak, Violetta
, (2020)
Green and sustainable chemistry approaches necessitate an ongoing investigation towards new, environmentally benign and selective catalysts. We have thus prepared a new benzothiazole-scaffolded hydrazone Schiff base ligand L and coordinated it with copper(II) ions leading to five different complexes, the form of which in the solid state is counterion-dependent. Nitrate, chloride and triflate anions lead to monometallic species, whereas utilization of sulfates and tetrafluoroborates is responsible for the formation of bimetallic assemblies. The catalytic efficiency of synthesized compounds was shown in Cu-TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-l-piperidinoxyl) aerobic oxidation of activated alcohols resulting in good to excellent conversions and 100% selectivity to form the corresponding aldehydes. Considering the experimental results and Density Functional Theory calculations we propose two most plausible reaction mechanisms that further corroborate the enhanced activity of bimetallic species. It appears that the tridentate character of the ligand sacrifices some of the overall catalytic efficiency for the selectivity of the process. Aqueous reaction medium, low catalyst loading, air as oxidant and exclusive oxidative selectivity render these CuII complexes promising candidates for further improvement.
Polymerization-Enhanced Photosensitization
Wu, Wenbo,Mao, Duo,Xu, Shidang,Kenry,Hu, Fang,Li, Xueqi,Kong, Deling,Liu, Bin
, p. 1937 - 1951 (2018)
Effective photosensitizers are highly desirable in many applications, such as photodynamic therapy, photocatalytic organic waste decomposition, and synthetic chemistry. Herein, we demonstrate polymerization-enhanced photosensitization, in which conjugated-polymer-based photosensitizers show much higher efficiency in singlet oxygen (1O2) production than their small-molecule analogs. Based on small-molecule photosensitizers SM1–SM4 with long wavelength emission, four conjugated polymer photosensitizers, CP1–CP4, were prepared. Interestingly, the conjugated polymer photosensitizers CP1–CP4 showed 5.06-, 5.07-, 1.73-, and 3.42-fold higher 1O2 generation efficiency than SM1–SM4, respectively. The improved intersystem crossing process from the singlet excitation states to the triplet excitation states and improved light-harvesting ability are essential to the enhancement of 1O2 generation efficiency. To illustrate the advantages of conjugated polymer photosensitizers on various applications, we demonstrate the superior performance of CP1 by using photoinduced organic waste decomposition, photoinduced organic oxidation reaction, and photodynamic cancer therapy as examples. Organic photosensitizers (PSs) are unique compounds that can absorb light or electromagnetic waves and transform them into reactive molecules, such as singlet oxygen (1O2). Highly efficient PSs are in great demand for many applications, such as photodynamic therapy, photoinduced organic waste decomposition, and photocatalytic organic synthesis. In this work, we propose the concept of polymerization-enhanced photosensitization. We show that polymerization of small-molecule PSs into conjugated polymers could significantly enhance their efficiency in 1O2 production with superior performance to that of commercial PSs (e.g., Ce6) in various applications. This concept is anticipated to open up new opportunities for rational photosensitizer design and applications. Effective photosensitizers are highly desirable in many applications. Herein, Liu and co-workers demonstrate polymerization-enhanced photosensitization, in which conjugated-polymer-based photosensitizers show much higher efficiency in singlet oxygen (1O2) production than their small-molecule analogs. Based on this concept, conjugated polymer photosensitizer CP1 with an aggregation-induced emission feature is proposed to show highly efficient 1O2 generation ability superior to that of its small-molecule analog SM1 and commercial photosensitizer Ce6 in photodynamic therapy, organic waste decomposition, and photocatalytic reactions.
Efficient synthesis of aromatic carboxylic acids from aryl ketones in ionic liquid
Jong, Chan Lee,Jang, Mi Lee
, p. 1071 - 1074 (2006)
Conversion of aryl ketones to the corresponding aromatic carboxylic acids has been achieved using sequential treatment of HDNIB and urea-hydrogen peroxide in [bmim]BF4 ionic liquid. Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Synthesis and evaluation of indole-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene ligands
Yan, Huan,Liu, Zhongxian,Tan, Kai,Ji, Ruigeng,Ye, Yingxin,Yan, Tingbing,Shen, Yuehai
, (2020)
Indole-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene ligands were synthesized and evaluated through both computational and experimental methods. The performances of medium-sized imidazolylidenes IIn3 and IIn4 were comparable to IPr in the Cu(I)-catalyzed carboxylation of organoboronic esters.
Active-sodium-promoted reductive cleavage of halogenated benzoic acids
Azzena, Ugo,Dettori, Giovanna,Mocci, Sarah,Pisano, Luisa,Cerioni, Giovanni,Mocci, Francesca
, p. 9171 - 9174 (2010)
The outcome of the reaction between 1,2-diaryl-1,2-disodioethanes and halogenated benzoic acids strongly depends on the nature of both reaction partners. Indeed, whilst chloro-, bromo- and iodobenzoic acids are easily dehalogenated, the reductive cleavage of fluorobenzoic acids proceeds to a high extent only in the presence of the dianions endowed with more powerful reducing properties. Moreover, it was observed that ortho-substituted benzoic acids are more easily dehalogenated than the corresponding para or meta isomers. These observations allowed the development of reaction conditions for the exhaustive or regioselective cleavage of selected polyhalogenated benzoic acids.
Transformation of Thioacids into Carboxylic Acids via a Visible-Light-Promoted Atomic Substitution Process
Fu, Qiang,Liang, Fu-Shun,Lou, Da-Wei,Pan, Gao-Feng,Wang, Rui,Wu, Min,Xie, Kai-Jun
supporting information, p. 2020 - 2024 (2022/03/31)
A visible-light-promoted atomic substitution reaction for transforming thiocacids into carboxylic acids with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as the oxygen source has been developed, affording various alkyl and aryl carboxylic acids in over 90% yields. The atomic substitution process proceeds smoothly through the photochemical reactivity of the formed hydrogen-bonding adduct between thioacids and DMSO. A DMSO-involved proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) and the simultaneous generation of thiyl and hydroxyl radicals are proposed to be key steps for realizing the transformation.
Mechanochemical Grignard Reactions with Gaseous CO2 and Sodium Methyl Carbonate**
Pfennig, Victoria S.,Villella, Romina C.,Nikodemus, Julia,Bolm, Carsten
supporting information, (2022/01/22)
A one-pot, three-step protocol for the preparation of Grignard reagents from organobromides in a ball mill and their subsequent reactions with gaseous carbon dioxide (CO2) or sodium methyl carbonate providing aryl and alkyl carboxylic acids in up to 82 % yield is reported. Noteworthy are the short reaction times and the significantly reduced solvent amounts [2.0 equiv. for liquid assisted grinding (LAG) conditions]. Unexpectedly, aryl bromides with methoxy substituents lead to symmetric ketones as major products.
Light-induced carboxylation of aryl derivatives with cooperative COF as an active photocatalyst and Ni(ii) co-catalyst
Chakrabortty, Pekham,Das, Anjan,Chowdhury, Arpita Hazra,Ghosh, Swarbhanu,Khan, Aslam,Islam, Sk. Manirul
, p. 4738 - 4745 (2021/03/22)
The photocatalytic carboxylation of aryl derivatives was demonstrated under CO2at atmospheric pressure using a mesoporous covalent organic framework (COF) as the active photocatalyst with triethylamine (TEA) as a sacrificial electron source under visible light. A yield of greater than 91% of the isolated product was achieved with 5 mg of catalyst. The reaction cycle is dependent on the use of the Ni(dmg)2co-catalyst and the sacrificial electron donor (TEA). The reaction does not occur in the absence of light (445 nm) even at elevated reaction temperature. We have also demonstrated that a yield of 32% of the isolated product could be obtained with the use of sunlight in the catalytic cycle. Additionally, this heterogeneous catalytic system was recyclable and reusable for several cycles.