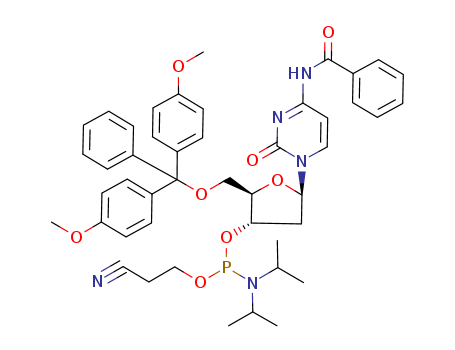
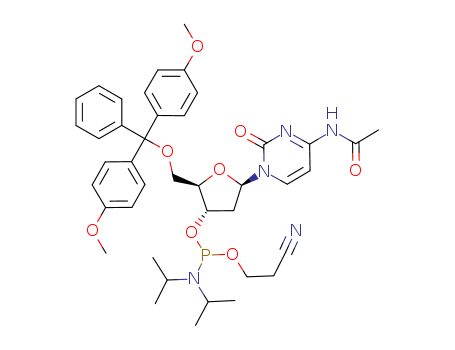
Deoxynucleotides and their analogs
Deoxynucleotides are molecules composed of a nitrogenous base (such as adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine), a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group. They serve as monomeric units that polymerize to form DNA, the genetic material in cells. Deoxynucleotides are essential for DNA replication, where they provide the building blocks for synthesizing new DNA strands during cell division and repair processes. Analogues of deoxynucleotides are structurally similar compounds that mimic the structure of natural deoxynucleotides but may have modified functional groups or chemical structures. These analogs can be synthesized to introduce specific properties such as enhanced stability, altered base-pairing specificity, or resistance to enzymatic degradation. Analogues of deoxynucleotides find extensive use in biomedical research and clinical applications, particularly in the development of antiviral drugs, anticancer agents, and tools for studying DNA replication and repair mechanisms. Their ability to selectively interfere with DNA synthesis or repair processes makes them valuable tools for understanding and treating genetic diseases and cancers.
- Structure
- Product name
- CAS No.
- Molecular formula
- Inquiry
![4-Amino-1-[(2R,3R,4R,5R)-3-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one](http://file1.lookchem.com/cas/reactions/2021/06/18/619217.png)