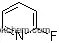Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 110-00-9 |
|---|---|
| Name: | Furan |
| Article Data: | 303 |
| Molecular Structure: | |
|
|
|
| Formula: | C4H4O |
| Molecular Weight: | 68.0752 |
| Synonyms: | Divinyleneoxide;Furfuran;Oxacyclopentadiene;Oxole;Tetrole; |
| EINECS: | 203-727-3 |
| Density: | 0.942 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point: | -85.6 °C |
| Boiling Point: | 31.36 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point: | -35 °C |
| Solubility: | insoluble in water |
| Appearance: | clear colorless liquid |
| Hazard Symbols: |
 T, T,  F+ F+
|
| Risk Codes: | 45-12-19-20/22-38-48/22-52/53-68 |
| Safety: | 53-45-61 |
| Transport Information: | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| PSA: | 13.14000 |
| LogP: | 1.27960 |
- 144851-82-1METHYL2-AMINO-3-FLUOROBENZOATE
- 483366-12-7(2S,4R)-1-Boc-2-cyano-4-hydroxypyrrolidine
- 173606-50-3BOC-10-AMINODECANOIC ACID
- 361456-36-2METHYL (R)-(+)-ISOCYANATO-3-PHENYLPROPI&
- 5156-58-1N-(1-Benzyl-4-pipperidinyl)-N-phenylpropanamide HCl
- 81281-59-67-Benzylideneaminotheophylline
- 50288-62-5threo-Phenyl-2-piperidyl acetamide
- 82993-81-5D-threo-Ritalinic acid hydrochloride
- 47087-37-6Z-D-Glu-OMe
- 1219080-61-1IMIDAZOLE-2-BORONIC ACID

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With carbon dioxide; palladium/alumina at 145℃; under 45004.5 Torr; for 6.5h; Green chemistry; | 99% |
| With carbon dioxide; 5% Pd(II)/C(eggshell) at 250℃; under 112511 Torr; Supercritical conditions; | 98% |
| With palladium nanoparticles deposited on porous SBA-15 In cyclohexane at 150℃; for 24h; Molecular sieve; | 96% |
- 82660-71-7
2',6'-exo-spirodioxatricyclo<5.2.1.02,6>dec-8'-en-3'-one>

A
- 110-00-9
furan

B
- 5732-90-1
1-oxaspiro<4.4>non-3-en-2-one

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| In tetrahydrofuran at 130℃; | A n/a B 98% |

A
- 110-00-9
furan

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| at 120℃; for 0.25h; Irradiation; | A n/a B 98% |

A
- 110-00-9
furan

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| at 120℃; for 0.25h; Irradiation; | A n/a B 98% |

A
- 110-00-9
furan

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| at 140℃; for 0.166667h; Irradiation; | A n/a B 98% |

A
- 110-00-9
furan

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| at 120℃; for 0.25h; Irradiation; | A n/a B 98% |

A
- 110-00-9
furan

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| at 140℃; for 0.166667h; Irradiation; | A n/a B 98% |
- 82660-72-8
2',6'-exo-spirodioxatricyclo<5.2.1.02,6>dec-8'-en-3'-one>

A
- 110-00-9
furan

B
- 4435-19-2
1-oxa-spiro[4.5]dec-3-en-2-one

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| In tetrahydrofuran at 130℃; under 7 Torr; | A n/a B 97% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| tetra-n-heptylammonium iodide; tributyltin iodide In para-xylene at 109 - 117℃; for 0.75h; | A 96.1% B n/a C n/a |

- 25414-22-6
2-methoxyfuran

- 123-73-9
trans-Crotonaldehyde

- 346440-54-8
(2S,5S)-5-benzyl-2-(tert-butyl)-3-methylimidazolidin-4-one

- 110-00-9
furan

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| In diethyl ether; chloroform | 95% |

- 643-12-9D-chiro-Inositol
- 61788-45-2Amines, hydrogenated tallow alkyl
- 106-88-71,2-Epoxybutane
- 24887-06-7Zinc formaldehyde sulfoxylate
- 7440-36-0Antimony
- 9000-01-5Arabic gum
- 9003-55-8Benzene, ethenyl-, polymer with 1,3-butadiene
- 64-67-5Diethyl sulfate
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
Chemistry
Molecular Structure:
.png)
Molecular Formula: C4H4O
Molecular Weight: 68.074
IUPAC Name: Furan
Synonyms of Furan (CAS NO.110-00-9): 1,4-Epoxy-1,3-butadiene ; 5-17-01-00291 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) ; AI3-24244 ; Axole ; BRN 0103221 ; CCRIS 3159 ; Divinylene oxide ; EINECS 203-727-3 ; Furfuran ; HSDB 89 ; NCI-C56202 ; Oxacyclopentadiene ; Oxole ; RCRA waste number U124 ; Tetrole ; Furan [UN2389] [Flammable liquid] ; UN2389
CAS NO: 110-00-9
Classification Code: Mutation data ; Reproductive Effect ; Tumor data
Melting point: -85.6 °C
Index of Refraction: 1.427
Molar Refractivity: 18.55 cm3
Molar Volume: 72.2 cm3
Surface Tension: 24.8 dyne/cm
Density: 0.942 g/cm3
Enthalpy of Vaporization: 27.1 kJ/mol
Boiling Point: 31.4 °C at 760 mmHg
Vapour Pressure: 605 mmHg at 25°C
Furan is aromatic because one of the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom is delocalized into the ring, creating a 4n+2 aromatic system similar to benzene. Because of the aromaticity, the molecule is flat and lacks discrete double bonds. The other lone pair of electrons of the oxygen atom extends in the plane of the flat ring system. The sp2 hybridization is to allow one of the lone pairs of oxygen to reside in a p orbital and thus allow it to interact within the pi-system.
History
In 1780 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, the first Furan (CAS NO.110-00-9) derivative to be described was 2-furoic acid. Another important derivative, furfural, was reported by Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner in 1831 and characterised nine years later by John Stenhouse. Furan itself was first prepared by Heinrich Limpricht in 1870, although he called it tetraphenol.
Uses
Furan (CAS NO.110-00-9) is mainly used to produce large quantities of hot-box process core Binder.
Production
Furan can be obtained from FURFURAL by oxidation and decarboxylation of the resulting furan-2-carboxylic acid, the FURFURAL being derived by destructive distillation of corn cobs in the presence of SULFURIC ACID.
the Feist-Benary synthesis is the organic synthesis of classic furan.
and there is a simple synthesis methods for furans is the reaction of 1,4-diketones with PHOSPHORUS PENTOXIDE in the Paal-Knorr Synthesis. It is interesting that the Thiophene formation reaction of 1,4-diketones with Lawesson's reagent also forms furans as side products.
Toxicity Data With Reference
| Organism | Test Type | Route | Reported Dose (Normalized Dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dog | LDLo | intravenous | 140mg/kg (140mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD BLOOD: HEMORRHAGE | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Vol. 26, Pg. 281, 1926. |
| dog | LDLo | oral | 234mg/kg (234mg/kg) | GASTROINTESTINAL: CHANGES IN STRUCTURE OR FUNCTION OF SALIVARY GLANDS GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING BLOOD: HEMORRHAGE | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Vol. 26, Pg. 281, 1926. |
| mouse | LC50 | inhalation | 120mg/m3/1H (120mg/m3) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES | American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal. Vol. 40, Pg. 310, 1979. |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 7mg/kg (7mg/kg) | American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal. Vol. 40, Pg. 310, 1979. | |
| rabbit | LDLo | oral | 234mg/kg (234mg/kg) | GASTROINTESTINAL: CHANGES IN STRUCTURE OR FUNCTION OF SALIVARY GLANDS GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING BLOOD: HEMORRHAGE | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Vol. 26, Pg. 281, 1926. |
| rat | LC50 | inhalation | 3398ppm/1H (3398ppm) | SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: PTOSIS: EYE BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: DYSPNEA | Hazelton Laboratories, Reports. Vol. HLA468-102, Pg. 1987, |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 5200ug/kg (5.2mg/kg) | American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal. Vol. 40, Pg. 310, 1979. |
Safety Profile
Hazard Codes of Furan (CAS NO.110-00-9):  T,
T, F+
F+
Risk Statements: 45-12-19-20/22-38-48/22-52/53-68
R45: May cause cancer.
R12: Extremely flammable.
R19: May form explosive peroxides.
R20/22: Harmful by inhalation and if swallowed.
R38: Irritating to skin.
R48/22: Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure if swallowed.
R52/53: Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment.
R68: Possible risk of irreversible effects.
Safety Statements: 53-45-61
S53: Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.
S45: In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.)
S61: Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets.
RIDADR: UN 2811 6.1/PG 2
WGK Germany: 3
RTECS: OB3870000
F: 8-9-23
HazardClass: 3
PackingGroup: I
Specification
Behavior of Furan (CAS NO.110-00-9) is quite dissimilar to that of the more typical heterocyclic ethers such as tetrahydrofuran due to its aromaticity, .It is considerably more reactive than benzene in electrophilic substitution reactions, due to the electron-donating effects of the oxygen heteroatom. Examination of the resonance contributors shows the increased electron density of the ring, leading to increased rates of electrophilic substitution.