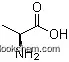
56-41-7Relevant articles and documents
Squamins C–F, four cyclopeptides from the seeds of Annona globiflora
Sosa-Rueda, Javier,Domínguez-Meléndez, Vanihamin,Ortiz-Celiseo, Araceli,López-Fentanes, Fernando C.,Cuadrado, Cristina,Fernández, José J.,Daranas, Antonio Hernández,Cen-Pacheco, Francisco
, (2021/08/04)
Four cyclic octapeptides, squamins C–F, were isolated from the seeds of Annona globiflora Schltdl. These compounds share part of their amino acid sequence, -Pro-Met(O)-Tyr-Gly-Thr-, with previously reported squamins A and B. Their structures were determined using NMR spectroscopic techniques together with quantum mechanical calculations (QM-NMR), ESI-HRMS data and a modified version of Marfey's chromatographic method. All compounds showed cytotoxic activity against DU-145 (human prostate cancer) and HeLa (human cervical carcinoma) cell lines. Clearly, A. globiflora is an important source of bioactive molecules, which could promote the sustainable exploitation of this undervalued specie.
Recreating the natural evolutionary trend in key microdomains provides an effective strategy for engineering of a thermomicrobial N-demethylase
Gu, Zhenghua,Guo, Zitao,Shao, Jun,Shen, Chen,Shi, Yi,Tang, Mengwei,Xin, Yu,Zhang, Liang
, (2022/03/09)
N-demethylases have been reported to remove the methyl groups on primary or secondary amines, which could further affect the properties and functions of biomacromolecules or chemical compounds; however, the substrate scope and the robustness of N-demethylases have not been systematically investigated. Here we report the recreation of natural evolution in key microdomains of the Thermomicrobium roseum sarcosine oxidase (TrSOX), an N-demethylase with marked stability (melting temperature over 100 C) and enantioselectivity, for enhanced substrate scope and catalytic efficiency on -C-N-bonds. We obtained the structure of TrSOX by crystallization and X-ray diffraction (XRD) for the initial framework. The natural evolution in the nonconserved residues of key microdomains—including the catalytic loop, coenzyme pocket, substrate pocket, and entrance site—was then identified using ancestral sequence reconstruction (ASR), and the substitutions that accrued during natural evolution were recreated by site-directed mutagenesis. The single and double substitution variants catalyzed the N-demethylation of N-methyl-L-amino acids up to 1800- and 6000-fold faster than the wild type, respectively. Additionally, these single substitution variants catalyzed the terminal N-demethylation of non-amino-acid compounds and the oxidation of the main chain -C-N- bond to a -C=N- bond in the nitrogen-containing heterocycle. Notably, these variants retained the enantioselectivity and stability of the initial framework. We conclude that the variants of TrSOX are of great potential use in N-methyl enantiomer resolution, main-chain Schiff base synthesis, and alkaloid modification or degradation.
Direct monitoring of biocatalytic deacetylation of amino acid substrates by1H NMR reveals fine details of substrate specificity
De Cesare, Silvia,McKenna, Catherine A.,Mulholland, Nicholas,Murray, Lorna,Bella, Juraj,Campopiano, Dominic J.
supporting information, p. 4904 - 4909 (2021/06/16)
Amino acids are key synthetic building blocks that can be prepared in an enantiopure form by biocatalytic methods. We show that thel-selective ornithine deacetylase ArgE catalyses hydrolysis of a wide-range ofN-acyl-amino acid substrates. This activity was revealed by1H NMR spectroscopy that monitored the appearance of the well resolved signal of the acetate product. Furthermore, the assay was used to probe the subtle structural selectivity of the biocatalyst using a substrate that could adopt different rotameric conformations.
Highly Stable Zr(IV)-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks for Chiral Separation in Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography
Jiang, Hong,Yang, Kuiwei,Zhao, Xiangxiang,Zhang, Wenqiang,Liu, Yan,Jiang, Jianwen,Cui, Yong
supporting information, p. 390 - 398 (2021/01/13)
Separation of racemic mixtures is of great importance and interest in chemistry and pharmacology. Porous materials including metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have been widely explored as chiral stationary phases (CSPs) in chiral resolution. However, it remains a challenge to develop new CSPs for reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC), which is the most popular chromatographic mode and accounts for over 90% of all separations. Here we demonstrated for the first time that highly stable Zr-based MOFs can be efficient CSPs for RP-HPLC. By elaborately designing and synthesizing three tetracarboxylate ligands of enantiopure 1,1′-biphenyl-20-crown-6, we prepared three chiral porous Zr(IV)-MOFs with the framework formula [Zr6O4(OH)8(H2O)4(L)2]. They share the same flu topological structure but channels of different sizes and display excellent tolerance to water, acid, and base. Chiral crown ether moieties are periodically aligned within the framework channels, allowing for stereoselective recognition of guest molecules via supramolecular interactions. Under acidic aqueous eluent conditions, the Zr-MOF-packed HPLC columns provide high resolution, selectivity, and durability for the separation of a variety of model racemates, including unprotected and protected amino acids and N-containing drugs, which are comparable to or even superior to several commercial chiral columns for HPLC separation. DFT calculations suggest that the Zr-MOF provides a confined microenvironment for chiral crown ethers that dictates the separation selectivity.
Inherently chiral dialkyloxy-calix[4]arene acetic acids as enantiodiscriminating additives for high-performance liquid chromatography separation of d,l-amino acids
Kalchenko, Olga I.,Trybrat, Oleksandr O.,Yesypenko, Oleksandr A.,Dyakonenko, Viktoriya V.,Shishkina, Svitlana V.,Kalchenko, Vitali I.
, p. 722 - 730 (2021/08/26)
Inherently chiral dialkyloxy-calix[4]arene acetic acids with asymmetric placement of substituents on the lower rim of the macrocycle were first studied as enantiodiscriminating additives to the mobile phase MeCN/H2O/HCOOH (75/25/0.02 by volume) in the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separation of d,l-alanine and d,l-valine on the achiral stationary phase ZORBAX Original CN. The dependence of enantio-binding properties on the position of alkyl groups is demonstrated. The highest resolution (1.65) and enantioselectivity (1.80) were obtained for the 1,2-dipropyloxy-calix[4]arene acetic acid.
Biosynthesis ofl-alanine fromcis-butenedioic anhydride catalyzed by a triple-enzyme cascadeviaa genetically modified strain
Cui, Ruizhi,Liu, Zhongmei,Yu, Puyi,Zhou, Li,Zhou, Zhemin
supporting information, p. 7290 - 7298 (2021/09/28)
In industry,l-alanine is biosynthesized using fermentation methods or catalyzed froml-aspartic acid by aspartate β-decarboxylase (ASD). In this study, a triple-enzyme system was developed to biosynthesizel-alanine fromcis-butenedioic anhydride, which was cost-efficient and could overcome the shortcomings of fermentation. Maleic acid formed bycis-butenedioic anhydride dissolving in water was transformed tol-alanineviafumaric acid andl-asparagic acid catalyzed by maleate isomerase (MaiA), aspartase (AspA) and ASD, respectively. The enzymatic properties of ASD from different origins were investigated and compared, as ASD was the key enzyme of the triple-enzyme cascade. Based on cofactor dependence and cooperation with the other two enzymes, a suitable ASD was chosen. Two of the three enzymes, MaiA and ASD, were recombinant enzymes cloned into a dual-promoter plasmid for overexpression; another enzyme, AspA, was the genomic enzyme of the host cell, in which AspA was enhanced by a T7promoter. Two fumarases in the host cell genome were deleted to improve the utilization of the intermediate fumaric acid. The conversion of whole-cell catalysis achieved 94.9% in 6 h, and the productivity given in our system was 28.2 g (L h)?1, which was higher than the productivity that had been reported. A catalysis-extraction circulation process for the synthesis ofl-alanine was established based on high-density fermentation, and the wastewater generated by this process was less than 34% of that by the fermentation process. Our results not only established a new green manufacturing process forl-alanine production fromcis-butenedioic anhydride but also provided a promising strategy that could consider both catalytic ability and cell growth burden for multi-enzyme cascade catalysis.
Leveraging Peptaibol Biosynthetic Promiscuity for Next-Generation Antiplasmodial Therapeutics
Lee, Jin Woo,Collins, Jennifer E.,Wendt, Karen L.,Chakrabarti, Debopam,Cichewicz, Robert H.
supporting information, p. 503 - 517 (2021/03/01)
Malaria remains a worldwide threat, afflicting over 200 million people each year. The emergence of drug resistance against existing therapeutics threatens to destabilize global efforts aimed at controlling Plasmodium spp. parasites, which is expected to leave vast portions of humanity unprotected against the disease. To address this need, systematic testing of a fungal natural product extract library assembled through the University of Oklahoma Citizen Science Soil Collection Program has generated an initial set of bioactive extracts that exhibit potent antiplasmodial activity (EC50 25 μM, selectivity index > 250). The unique chemodiversity afforded by these fungal isolates serves to unlock new opportunities for translating peptaibols into a bioactive scaffold worthy of further development.
Engineering the large pocket of an (S)-selective transaminase for asymmetric synthesis of (S)-1-amino-1-phenylpropane
Liu, He,Wang, Hualei,Wei, Dongzhi,Xie, Youyu,Xu, Feng,Xu, Xiangyang,Yang, Lin
, p. 2461 - 2470 (2021/04/22)
Amine transaminases offer an environmentally benign chiral amine asymmetric synthesis route. However, their catalytic efficiency towards bulky chiral amine asymmetric synthesis is limited by the natural geometric structure of the small pocket, representing a great challenge for industrial applications. Here, we rationally engineered the large binding pocket of an (S)-selective ?-transaminase BPTA fromParaburkholderia phymatumto relieve the inherent restriction caused by the small pocket and efficiently transform the prochiral aryl alkyl ketone 1-propiophenone with a small substituent larger than the methyl group. Based on combined molecular docking and dynamic simulation analyses, we identified a non-classical substrate conformation, located in the active site with steric hindrance and undesired interactions, to be responsible for the low catalytic efficiency. By relieving the steric barrier with W82A, we improved the specific activity by 14-times compared to WT. A p-p stacking interaction was then introduced by M78F and I284F to strengthen the binding affinity with a large binding pocket to balance the undesired interactions generated by F44. T440Q further enhanced the substrate affinity by providing a more hydrophobic and flexible environment close to the active site entry. Finally, we constructed a quadruple variant M78F/W82A/I284F/T440Q to generate the most productive substrate conformation. The 1-propiophenone catalytic efficiency of the mutant was enhanced by more than 470-times in terms ofkcat/KM, and the conversion increased from 1.3 to 94.4% compared with that of WT, without any stereoselectivity loss (ee > 99.9%). Meanwhile, the obtained mutant also showed significant activity improvements towards various aryl alkyl ketones with a small substituent larger than the methyl group ranging between 104- and 230-fold, demonstrating great potential for the efficient synthesis of enantiopure aryl alkyl amines with steric hindrance in the small binding pocket.
Method for photolysis of amido bonds
-
Paragraph 0046; 0048-0049; 0086-0089, (2021/06/26)
The invention discloses a method for photo-splitting amido bonds, wherein the method is mild in reaction condition and can realize splitting of amido bonds by using illumination. The method for photo-splitting the amido bonds comprises the following steps: reacting 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene with an amino group of a substance which contains alpha amino acid at the tail end and is shown as a structural formula I to generate a compound 1 represented by a structural formula II; and under light irradiation, carrying out amido bond cleavage reaction on the compound 1, wherein R1 is a side chain group of alpha-amino acid, and R2 is aryl, aliphatic hydrocarbon, -CH(R)-COOH or polypeptide.
Targeted Isolation of Asperheptatides from a Coral-Derived Fungus Using LC-MS/MS-Based Molecular Networking and Antitubercular Activities of Modified Cinnamate Derivatives
Chao, Rong,Hou, Xue-Mei,Xu, Wei-Feng,Hai, Yang,Wei, Mei-Yan,Wang, Chang-Yun,Gu, Yu-Cheng,Shao, Chang-Lun
, p. 11 - 19 (2021/01/14)
Under the guidance of MS/MS-based molecular networking, four new cycloheptapeptides, namely, asperheptatides A-D (1-4), were isolated together with three known analogues, asperversiamide A-C (5-7), from the coral-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. The planar structures of the two major compounds, asperheptatides A and B (1 and 2), were determined by comprehensive spectroscopic data analysis. The absolute configurations of the amino acid residues were determined by advanced Marfey's method. The two structurally related trace metabolites, asperheptatides C and D (3 and 4), were characterized by ESI-MS/MS fragmentation methods. A series of new derivatives (8-26) of asperversiamide A (5) were semisynthesized. The antitubercular activities of 1, 2, and 5-26 against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra were also evaluated. Compounds 9, 13, 23, and 24 showed moderate activities with MIC values of 12.5 μM, representing a potential new class of antitubercular agents.