31431-39-7 Usage
Pharmacology and mechanism of action
Mebendazole is a benzimidazole derivative with a broad spectrum of anthelminthic activity. It is highly effective against adult and larval stages of Ascaris lumbricoides, Enterobius vermicularis, Trichuris trichiura, hookworms (Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus) and Capillaria philippinensis. It is also ovicidal against Ascaris lumbricoides and Trichuris trichuria [1]. With high doses, the drug has some effect against hydatid disease [2]. Recent in vitro studies have reported mebendazole to be more effective than metronidazole in killing Giardia lamblia [3,4]; however, clinical findings are inconclusive [5, 6, 7]. The mechanisms of action of benzimidazoles are similar. These drugs appear to bind to parasite tubules with subsequent inhibition of the polymerization of tubules to microtubules which is vital for the normal functioning of the parasite cells[8].
Indications
Different sources of media describe the Indications of 31431-39-7 differently. You can refer to the following data:
1. Mebendazole is the drug of choice for mixed nematode infections due to Trichuris trichiura, Ascaris lumbricoides, Enterobius vermicularis, Capillaria philippinensis or hookworms. The drug may be used against hydatid disease when albendazole is not available.
2. Unlike thiabendazole, mebendazole (Vermox) does not
inhibit fumarate reductase.While mebendazole binds to
both mammalian and nematode tubulin, it exhibits a
differential affinity for the latter, possibly explaining the
selective action of the drug. The selective binding to
nematode tubulin may inhibit glucose absorption, leading
to glycogen consumption and ATP depletion.
Side effects
Different sources of media describe the Side effects of 31431-39-7 differently. You can refer to the following data:
1. Despite the widespread use of the drug, few side effects have been reported, especially in patients with heavy infections. These include transitory abdominal pain, diarrhoea and slight headache. High doses of the drug such as those used in the treatment of hydatid disease have been associated with bone marrow toxicity, alopecia, hepatitis, glomerulonephritis, fever and exfoliative dermatitis [9–12].
2. Abdominal discomfort and diarrhea may occur
when the worm load is heavy. Its use is contraindicated
during pregnancy.
3. Diarrhea and gastrointestinal discomfort may occur, but
adverse reactions are generally mild. Woman of childbearing
age should be informed of a potential risk to the fetus if treated
during pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester.
Contraindications and precautions
When high doses of mebendazole are given, regular monitoring of serum-transaminase levels and leukocyte and platelet counts must be carried out. In patients with liver impairment dosage reductions must be made.
Interactions
The concomitant administration of phenytoin or carbamazepine has been reported to lower the plasma concentration of mebendazole [12], while cimetidine had the opposite effect[13].
Preparations
? Pantelmin? (Janssen). Oral solution 20 mg/ml. Tablets 100 mg, 500 mg. ? Vermox? (Janssen). Oral suspension 20 mg/ml. Tablets 100 mg, 500 mg. Several other preparations are available.
Reference
1. Van den Bossche H, Rochette F, Horig C (1982). Mebendazole and related anthelminthics. Adv Pharmacol Chemother, 19, 287–296.
2. Todorov T, Vutova K, Mechkov G, Georgiev P, Petkov D, Tonchev Z, Nedelkov G (1992). Chemotherapy of human cystic echinococcosis: comparative efficacy of mebendazole and albendazole. Ann Trop Med Parasitol, 86, 59–66.
3. Cedillo-Rivera R, Munoz O (1992). In-vitro susceptibility of Giardia lamblia to albendazole, mebendazole and other chemotherapeutic agents. J Med Microbiol, 37, 221–224.
4. Edlind TD, Hang TL, Chakraborty PR (1990). Activity of the anthelminthic benzimidazoles against Giardia lamblia in vitro. J Infect Dis, 162, 1408–1411.
5. Al-Waili D, Al-Waili B, Saloom K (1988). Therapeutic use of mebendazole in giardial infections. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 82, 438.
6. Al-Waili NSD, Hasan NU (1992). Mebendazole in giardial infections: A comparative study with metronidazole. J Infect Dis, 165, 1170–1171.
7. Gascon J, Moreno A, Valls ME, Miro JM, Corachan M (1989). Failure of mebendazole treatment in Giardia lamblia infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 83, 647.
8. Lacey E (1990). Mode of action of Benzimidazoles. Parasitology Today, 6, 112–115.
9. Wilson JF, Rausch RL, McMahon BJ, Schantz PM (1992). Parasitological effect of chemotherapy in alveolar hydatid disease: Review of experience with mebendazole and albendazole in Alaskan eskimos. Clin. Infect Dis, 15, 234–249.
10. Ellis M, von Sinner W, Al-hokail A, Siek JA (1992). Clinical-radiological evaluation of benzimidazoles in the management of Echinococcus granulosus cysts. Scand J Infect Dis, 24, 1–13.
11. Todorov T, Vutova K, Mechkov G, Tonchev Z, Georgiev P, Lazarova I (1992). Experience in the chemotherapy of severe, inoperable echinococcosis in man. Infection, 20, 23–24.
12. Luder PJ, Siffert B, Witassek F, Meister F, Bircher J (1986). Treatment of hydatid disease with high oral doses of mebendazole. Long-term follow-up of plasma mebendazole levels and drug interactions. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 31, 443–448.
13. Bekhti A, Pirotte J (1987). Cimetidine increases serum mebendazole concentrations. Implications for treatment of hepatic hydatid cysts. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 24, 390–392.
Description
Mebendazole is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic that is active against both larval and adult stages of nematodes selectively binding the β-subunit of tubulin, thereby inhibiting intestinal microtubule synthesis in the parasite (IC50 = 0.19 μM for Giardia in vitro). As a tubulin-binding agent, mebendazole also possesses antitumor properties, inducing apoptosis of various human carcinomas both in vitro and in vivo, thus preventing their growth and migration. Furthermore, mebendazole has been used to inhibit hedgehog signaling in cancer cells via suppression of the formation of the primary cilium, a microtubule-based organelle that functions as a signaling hub for hedgehog pathway activation. Additionally, mebendazole has been shown to stabilize the transcriptional activator HIF-1α and its downstream targets, abrogating oxidative neuronal death in primary neurons.
Chemical Properties
White Amorphous Powder
Originator
Vermox,Ortho,US ,1975
Uses
Different sources of media describe the Uses of 31431-39-7 differently. You can refer to the following data:
1. Mebendazole Polymorph C is an Anthelmintic (Nematodes).
2. Anthelmintic (Nematodes)
3. For the treatment of Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm), Trichuris trichiura (whipworm), Ascaris lumbricoides (common roundworm), Ancylostoma duodenale (common hookworm), Necator americanus (American hookworm) in single or mixed infections.
Definition
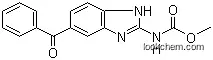
ChEBI: A carbamate ester that is methyl 1H-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate substituted by a benzoyl group at position 5.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 5.2 parts of 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzophenone, 5 parts of ammonia, 72 parts of methanol and 13 parts of sulfolane is heated overnight at 125°C in a sealed tube. The reaction mixture is evaporated in vacuo. The semisolid residue is boiled in 100 parts of a diluted hydrochloric acid solution. After cooling, the precipitated product is filtered off and dissolved in chloroform. The chloroform phase is dried and evaporated. The residue is crystallized from toluene, yielding 4-amino-3-nitrobenzophenone; MP 141°C.A mixture of 9.6 parts of 4-amino-3-nitrobenzophenone, 160 parts of
methanol, 8 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 part of palladiumon-charcoal catalyst 10% is hydrogenated at normal pressure and at room
temperature. After the calculated amount of hydrogen is taken up,
hydrogenation is stopped. The catalyst is filtered off and the solvent is
evaporated. The solid residue is triturated in 2-propanol. The latter is partly
evaporated and the solid product is filtered off, washed with 2-propanol and
dried, yielding 3,4-diaminobenzophenone hydrochloride; MP 207°C.7.8 parts of S-methylisothiourea sulfate are stirred in 10 parts of water in an
ice bath and there are added 4.5 parts of methyl chloroformate. While
keeping the temperature below 20°C, there are added dropwise, in the course
of 10 minutes, 17 parts of sodium hydroxide solution 25% (pH 8±), followed
by the addition of 5.6 parts of acetic acid (pH 5). To this mixture is added at
20°C a suspension of 7 parts of 3,4-diaminobenzophenone hydrochloride in
100 parts of water, followed by the addition of 2.3 parts of sodium acetate.The whole is slowly heated to 85°C and stirred at this temperature for 45
minutes. The reaction mixture is cooled and the precipitated product is filtered
off. It is washed successively with water and ethanol, dried and crystallized from a mixture of acetic acid and methanol, yielding methyl N-[5(6)-benzoyl2-benzimidazolyl]carbamate; MP 288.5°C.
Brand name
Vermox (McNeil).
Therapeutic Function
Anthelmintic
General Description
White to slightly yellow powder. Pleasant taste. Practically water insoluble.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Mebendazole is a carbamate ester-amine. Amines behave as chemical bases. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Mebendazole are not available; however, Mebendazole is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A benzimidazole carbamic acid methyl ester available for oral
administration. It is insoluble in water and stable at room
temperature.
Mechanism of action
Mebendazole is given orally; it is poorly soluble, and
very little is absorbed from the intestinal tract. About 5
to 10%, principally the decarboxylated derivatives, is
recovered in the urine; most of the orally administered
drug is found in the feces within 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption is poor. Plasma concentrations achieved after
oral administration of 100 mg every 12 h for three consecutive
days do not exceed 0.03 mg/L. All metabolites are inactive.
Most of the dose, as unchanged drug or a primary metabolite,
is retained in the intestinal tract and passed in the feces, with
the remainder, approximately 2% of the dose, excreted in the
urine.
Clinical Use
Different sources of media describe the Clinical Use of 31431-39-7 differently. You can refer to the following data:
1. Methyl 5-benzoyl-2-benzimidazolecarbamate (Vermox) isa broad-spectrum anthelmintic that is effective against variousnematode infestations, including whipworm, pinworm,roundworm, and hookworm. Mebendazole irreversiblyblocks glucose uptake in susceptible helminths, thereby depletingglycogen stored in the parasite. It apparently does notaffect glucose metabolism in the host. It also inhibits cell divisionin nematodes.Mebendazole is poorly absorbed by the oral route.Adverse reactions are uncommon and usually consist of abdominaldiscomfort. It is teratogenic in laboratory animalsand, therefore, should not be given during pregnancy.
2. Mebendazole is used primarily for the treatment of
A. lumbricoides, T. trichiura, E. vermicularis, and hookworm
infections, in which it produces high cure rates. It
is an alternative agent for the treatment of trichinosis
and visceral larva migrans. Owing to its broad-spectrum
anthelmintic effect, mixed infections (ascariasis, hookworm
infestation, or enterobiasis in association with
trichuriasis) frequently respond to therapy. High doses
have been used to treat hydatid disease, but albendazole
is now thought to be superior.
3. Intestinal nematode infections
Trichinosis (larval stage)
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by
ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human
mutation data reported. An experimental
teratogen. Experimental reproductive
effects. When heated to decomposition it
emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also
CARBAMATES.
Synthesis
Mebendazole, methyl-[5-(benzoyl)-1H-benzoimidazol-2-yl]carbamate (38.1.5), is a derivative of benzoimidazole, which is made by reacting 3,4-diaminobenzophenone (38.1.3) with N-methoxycarbonyl-S-methylthiourea (38.1.4).
The necessary reagents are made in the following manner. Nitration of 4-chlorobenzo�phenone with nitric acid at a temperature lower than 5°C gives 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzophenone (38.1.1), in which the chlorine atom is replaced with an amino group by heating it to 125°C in a solution of ammonia in methanol to make 4-amino-3-nitrobenzophenone (38.1.2). Reducing the nitro groups in this compound with hydrogen using a palladium on carbon cata�lyst gives 3,4-diaminobenzophenone (38.1.3).
The second reagent, N-methoxycarbonyl-S-methylthiourea (38.1.4), is made by reacting methyl chloroformate with S-methylthiourea.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Cimetidine: possibly inhibits metabolism of
mebendazole.
Antiepileptics: phenytoin, carbamazepine and
phenobarbital: lower mebendazole concentrations,
only relevant when being used in high doses for
echinococcosis.
references
[1]. seo bs, cho sy, kang sy, et al. anthelmintic efficacy of methyl-5-benzoylbenzimidazole-2-carbamate(mebendazole) against multiple helminthic infections. kisaengchunghak chapchi. 1977 jun;15(1):11-16.[2]. morgan um, reynoldson ja, thompson rc. activities of several benzimidazoles and tubulin inhibitors against giardia spp. in vitro. antimicrob agents chemother. 1993 feb;37(2):328-31.[3]. doudican n, rodriguez a, osman i, et al. mebendazole induces apoptosis via bcl-2 inactivation in chemoresistant melanoma cells. mol cancer res. 2008 aug;6(8):1308-15.[4]. mukhopadhyay t, sasaki j, ramesh r, et al. mebendazole elicits a potent antitumor effect on human cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo. clin cancer res. 2002 sep;8(9):2963-9.[5]. sasaki j, ramesh r, chada s, et al. the anthelmintic drug mebendazole induces mitotic arrest and apoptosis by depolymerizing tubulin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. mol cancer ther. 2002 nov;1(13):1201-9.[6]. larsen ar, bai ry, chung jh, et al. repurposing the antihelmintic mebendazole as a hedgehog inhibitor. mol cancer ther. 2015 jan;14(1):3-13. [7]. aleyasin h, karuppagounder ss, kumar a, et al. antihelminthic benzimidazoles are novel hif activators that prevent oxidative neuronal death via binding to tubulin. antioxid redox signal. 2015 jan 10;22(2):121-34.
Check Digit Verification of cas no
The CAS Registry Mumber 31431-39-7 includes 8 digits separated into 3 groups by hyphens. The first part of the number,starting from the left, has 5 digits, 3,1,4,3 and 1 respectively; the second part has 2 digits, 3 and 9 respectively.
Calculate Digit Verification of CAS Registry Number 31431-39:
(7*3)+(6*1)+(5*4)+(4*3)+(3*1)+(2*3)+(1*9)=77
77 % 10 = 7
So 31431-39-7 is a valid CAS Registry Number.
InChI:InChI=1/C16H13N3O3/c1-22-16(21)19-15-17-12-8-7-11(9-13(12)18-15)14(20)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-9H,1H3,(H2,17,18,19,21)
31431-39-7Relevant articles and documents
Method for synthesizing mebendazole by means of methyl cyanocarbamate
-
Paragraph 0025-0042; 0051-0056, (2019/10/10)
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing mebendazole by means of methyl cyanocarbamate. The method comprises the steps that 3,4-diaminobenzophenone and methyl cyanocarbamate react in acetone and hydrochloric acid to prepare a crude mebendazole, the crude mebendazole forms salt in methyl alcohol-nitric acid to obtain mebendazole nitrate, and finally the mebendazole nitrate is subjected to crystal transformation in methyl alcohol-nitric acid to obtain C crystal type mebendazole. The cheap and easily-obtained 3,4-diaminobenzophenone and methyl cyanocarbamate are adopted as raw materials, a large quantity of waste salts generated in the O-methyl isourea methyl formate synthesis process are avoided, the cyclization time is short and only needs 4-6 h, the production period is remarkably shortened, high-salt wastewater by-products can be treated through simple distillation, and the good industrial prospect is achieved.
MEBENDAZOLE POLYMORPH FOR TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF TUMORS
-
, (2016/09/22)
Mebendazole is an antiparasitic drug with over 40 years of safe use. Recently mebendazole was repurposed for glioblastoma therapy. Three polymorphs of mebendazole exist, but the relative polymorph content for existing drugs varies, and the therapeutic anti-cancer relevance of the different polymorphs was unknown. As an oral drug mebendazole polymorph C is a superior form, and it reaches the brain and brain tumors in effective concentrations. Efficacy is further improved by combining mebendazole with a P-glycoprotein inhibitor. Mebendazole may also be used for therapy of other cancers, as well as a chemo-preventative agent.
DMSO-mediated ligand dissociation: Renaissance for biological activity of N-heterocyclic-[Ru(η6-arene)Cl2] drug candidates
Patra, Malay,Joshi, Tanmaya,Pierroz, Vanessa,Ingram, Katrin,Kaiser, Marcel,Ferrari, Stefano,Spingler, Bernhard,Keiser, Jennifer,Gasser, Gilles
, p. 14768 - 14772 (2013/11/06)
Slipped under the radar? 1HNMR spectroscopic examination revealed that [Ru(η6-arene)Cl2(L)] (L=N-heterocyclic ligands) complexes readily undergo a ligand exchange reaction in DMSO (see scheme), a popular medium for preparing stock solutions for biological screening. It is therefore highly important for researchers to study the stability in DMSO before reporting on the biological activity of such complexes. Copyright