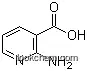
5345-47-1Relevant articles and documents
Preparation method of 2-aminopyridine-3-carboxylic acid
-
Paragraph 0015-0029, (2022/01/12)
The present invention discloses a method for preparing 2- aminopyridine-3-carboxylic acid, comprising the following steps: adding 500g of deionized water in a 1L three-mouth bottle, adding raw material 2-amino-3-methylpyridine 100g under stirring, adding a catalyst of 186g and heating to 55-65 ° C, and then controlling the temperature at 60-70 ° C in batches to add potassium permanganate 146g, after addition continue stirring reaction for 3 hours; then cooled to room temperature, filtered to remove black manganese dioxide and recovered After adjusting the PH to 2.5 in the aqueous phase, freezing to 3-7 ° C filtration, the white filter cake was obtained, and then washed and dried in ice water to give the product 2-amino 2-aminopyridine-3-carboxylic acid 65 grams. The preparation method of the intermediate 2-aminopyridine-3-carboxylic acid of this drug has reasonable design of the whole process, mild conditions, simple operation, easy raw materials and high generation efficiency. The reaction of this method is safe and controllable, and the obtained manganese dioxide by-products can be recycled, and the yield is high, which is conducive to industrial production.
Oxidation of Primary Alcohols and Aldehydes to Carboxylic Acids via Hydrogen Atom Transfer
Tan, Wen-Yun,Lu, Yi,Zhao, Jing-Feng,Chen, Wen,Zhang, Hongbin
supporting information, p. 6648 - 6653 (2021/09/08)
The oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes to the corresponding carboxylic acids is a fundamental reaction in organic synthesis. In this paper, we report a new chemoselective process for the oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes. This metal-free reaction features a new oxidant, an easy to handle procedure, high isolated yields, and good to excellent functional group tolerance even in the presence of vulnerable secondary alcohols and tert-butanesulfinamides.
Copper(ii)-catalyzed c-n coupling of aryl halides and n-nucleophiles promoted by quebrachitol or diethylene glycol
Chen, Guoliang,Chen, Yuanguang,Du, Fangyu,Fu, Yang,Wu, Ying,Zhou, Qifan
supporting information, p. 2161 - 2168 (2019/11/25)
Herein, we report the natural ligand quebrachitol (QCT) as a promoter for a Cu(II) catalyst, which is highly effective for N-Arylation of various amines and related aryl halides. A series of diarylamine derivatives were obtained in high yields by using diethylene glycol (DEG) as both ligand and solvent. The C-N coupling reactions proceed under mild conditions and exhibit good functional group tolerance.
Method for synthesizing 2-aminopyridin-3-carboxylic acid
-
Paragraph 0008; 0029, (2019/01/08)
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 2-aminopyridin-3-carboxylic acid. The method utilizes 2, 3-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, acetic anhydride, ammonia water, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, bromine, 2-amidopyridin-3-carboxylic acid, CNTs and SnCl2.2H2O as main raw materials. Through ammonium acetate solution washing and sulfuric acid sulfonation, SnO2 of the coating layer is converted into solid super acid S-SnO2 so that the stability of the system is improved and the catalytic activity of the catalyst is improved. The method utilizes cheap and easily available raw materials, is safe in operation, realizes simple separation and purification and a high product yield and is suitable for large-scale preparation.
Heterocyclic mutilin esters and their use as antibacterials
-
, (2008/06/13)
Pleuromutilin compounds of the formula: 1are of use in anti-bacterial therapy.
π-deficient 2-(arylsulfonyl)ethyl esters as protecting groups for carboxylic acids
Alonso, Diego A.,Nájera, Carmen,Varea, Montserrat
, p. 277 - 287 (2007/10/03)
Several π-deficient 2-(arylsulfonyl)ethyl groups have been studied as carboxylic acid protecting groups. The 2-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenylsulfonyl]ethyl group is the most easily removed protecting group for acids under mild basic conditions using aqueous NaHCO3.
Pyridazinone derivatives and processes for preparing the same
-
, (2008/06/13)
Disclosed is a pyridazinone compound represented by the formula (I): STR1 wherein X represents hydrogen atom or the like; Y represents a single bonding arm, oxygen atom or sulfur atom; A represents a straight or branched alkylene group which may have a double bond; B represents carbonyl group or thiocarbonyl group; and R2 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms which may be substituted or the like; or B represents sulfonyl group; and R2 represents a lower alkenyl group or the like; R1 represents hydrogen atom or the like; R3 represents hydrogen atom or the like; R4 represents hydrogen atom or the like; and R5 represents hydrogen atom or the like, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
A FACILE REARRANGEMENT OF PYRIDINECARBOHYDROXAMIC ACIDS IN FORMAMIDE
Eckstein, Zygmunt,Lipczynska-Kochany, Ewa,Krzeminski, Jerzy
, p. 1899 - 1901 (2007/10/02)
Five pyridinecarbohydroxamic acids were converted smoothly to the corresponding aminopyridines by means of the "amide modification" of the Lossen rearrangment.
Preparation of 2-aminopyridine derivatives
-
, (2008/06/13)
2-Aminopyridine derivatives are prepared by reacting a quaternary ammonium compound with malodinitrile in the presence of an alkanol, followed by reaction with ammonia in the presence of an alkanol, water and/or an ether to give aminonicotinonitrile and, if desired, then reacting this product with an alkali metal compound to give aminonicotinic acid. The 2-aminopyridine derivatives obtainable by the process of the invention are valuable starting materials for the preparation of pesticides, drugs, vitamins and dyes.
On derivatives of 4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine (author's transl)
Kretzschmar
, p. 253 - 256 (2007/10/02)
A typical representative of the hypnotic and anticonvulsive 4-quinazoline group is methaqualone (1). A number of new derivatives of 4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine (10) were synthetized by substituting the benzene ring in the quinazolone molecule by the pyridine ring. The synthesis was achieved by the condensation of 2-acetaminonicotinic acid (9) and a primary amine or by the reaction of 2-aminonicotinic acid (8) with acetic acid and a primary amine. These new compounds were tested on animals for antiphlogistic, analgetic and antipyretic activities and for effects on the central nervous system as well. It was tried to establish, on the basis of the results obtained, relations between the chemical constitution and the pharmacological efficacy. It was found that, depending on the nature of the substituents in the position 3; either the antiphlogistic, analgetic and antipyretic effects or the anticonvulsive action will prevail.