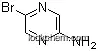
59489-71-3Relevant articles and documents
A novel luciferin-based bright chemiluminescent probe for the detection of reactive oxygen species
Sekiya, Maki,Umezawa, Keitaro,Sato, Akemi,Citterio, Daniel,Suzuki, Koji
, p. 3047 - 3049 (2009)
This communication reports the synthesis, chemiluminescence properties, and biological application of KEIO-BODIPY-imidazopyrazine (KBI), a yellow-green chemiluminescent probe for the detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated from living cells. The Royal Society of Chemistry 2009.
Long-range proton-coupled electron transfer in phenol-Ru(2,2′- bipyrazine)32+ dyads
Bronner, Catherine,Wenger, Oliver S.
, p. 3617 - 3622 (2014)
Two dyads in which either 4-cyanophenol or un-substituted phenol is connected via a p-xylene spacer to a Ru(bpz)32+ (bpz = 2,2′-bipyrazine) complex were synthesized and investigated. Selective photo-excitation of Ru(bpz)32+ at 532 nm in a CH 3CN-H2O mixture leads to the formation of 4-cyanophenolate or phenolate along with Ru(bpz)32+ in its electronic ground state. This apparent photoacid behavior can be understood on the basis of a reaction sequence comprised of an initial photoinduced proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) during which 4-cyanophenol or phenol is oxidized and deprotonated, followed by a thermal electron transfer event in the course of which 4-cyanophenoxyl or phenoxyl is reduced by Ru(bpz)3+ to 4-cyanophenolate or phenolate. Conceptually, this reaction sequence is identical to a sequence of photoinduced charge-separation and thermal charge-recombination events as observed previously for many electron transfer dyads, with the important difference that the initial photoinduced electron transfer process is proton-coupled. The dyad containing 4-cyanophenol reacts via concerted-proton electron transfer (CPET) whereas the dyad containing un-substituted phenol appears to react predominantly via a stepwise PCET mechanism. Long-range PCET is a key reaction in photosystem II. Understanding the factors that govern the kinetics of long-range PCET is desirable in the broader context of light-to-energy conversion by means of proton-electron separation across natural or artificial membranes.
Efficient Halogenation of 2-Aminopyrazine
Grima, Josep,Lizano, Enric,Pujol, M. Dolors
, p. 2000 - 2003 (2019/10/22)
2-Aminopyrazine was halogenated with NIS, NCS, and NBS under different reaction conditions. Chlorination and bromination were achieved with good yields by using acetonitrile as the solvent. However, iodination was only obtained in poor yields. Undoubtedly, the best conditions for both mono-and dihalogenation were the use of NBS, acetonitrile, and microwave assistance for short periods. 3,5-Dibromo-2-Aminopyrazine is an excellent functionalized starting material for the synthesis of nitrogen heterocycles.
CHEMILUMINESCENT IMIDAZOPYRAZINONE-BASED PHOTOSENSITIZERS WITH AVAILABLE SINGLET AND TRIPLET EXCITED STATES
-
Page/Page column 26; 27, (2019/11/19)
The present application describes the development of novel photosensitizers that can undergo self-excitation due to a chemiluminescent reaction, to produce readily-available singlet and/or triplet states and are composed by an imidazopyrazinone core. This core is functionalized with a variety of chromophores and spin converters, allowing to modulate the optical and photosensitizing properties. In one application, the chemiluminescent reaction is triggered by the superoxide anion, overexpressed in tumors, and by molecular oxygen, in aprotic solvents. The photosensitizers can be used in photodynamic therapy of cancer, without the need for external light sources and when triggered by a tumor marker, superoxide anion, while eliminating the restrictions of this therapy associated with tumor size and localization. The emission of light during the self-excitation reaction, and the resulting non-autofluorescence and low background noise, allow their use in tumor diagnostics. The photosensitizers can also be used without light sources and metal elements in photocatalysis reactions.
Discovery of pyrimidine nucleoside dual prodrugs and pyrazine nucleosides as novel anti-HCV agents
Guo, Shuang,Xu, Mingshuo,Guo, Qi,Zhu, Fuqiang,Jiang, Xiangrui,Xie, Yuanchao,Shen, Jingshan
, p. 748 - 759 (2019/01/26)
To explore the application potential of dual prodrug strategies in the development of anti-HCV agents, a variety of sofosbuvir derivatives with modifications at the C4 or N3 position of the uracil moiety were designed and synthesized. Some compounds exhibited potent anti-HCV activities, such as 4e and 8a–8c with similar EC50 values (0.20–0.22 μM) comparative to that of sofosbuvir (EC50 = 0.18 μM) in a genotype 1b based replicon Huh-7 cell line. Moreover, 8b displayed a good human plasma stability profile, and was easily metabolized in human liver microsomes expectantly. On the other hand, aiming to discover novel anti-HCV nucleosides, pyrazin-2(1H)-one nucleosides and their phosphoramidate prodrugs were investigated. Several active compounds were discovered, such as 25e (EC50 = 7.3 μM) and S-29b (EC50 = 19.5 μM). This kind of nucleosides were interesting and would open a new avenue for the development of antiviral agents.
REDUCTION OF PRO-INFLAMMATORY HDL USING A LEUKOTRIENE INHIBITOR
-
Paragraph 00202, (2018/09/12)
A method involving the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of a leukotriene inhibitor, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a pharmaceutically acceptable N-oxide, a pharmaceutically active metabolite, a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug, or pharmaceutically acceptable solvate thereof to a human for reducing a level of pro-inflammatory HDL in the human. Various examples of leukotriene inhibitors, including 3-[3-tert-butylsulfanyl-1-[4-(6-ethoxy-pyridin- 3-yl)-benzyl]-5-(5-methyl-pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)-1H-indol-2-yl]-2, 2-dimethyl-propionic acid, are disclosed for administration for the reduction of pro-inflammatory HDL in a human. Reduction of pro-inflammatory HDL by the leukotriene inhibitor may include conversion of at least a portion of pro-inflammatory HDL to anti-inflammatory HDL.
NOVEL COMPOUNDS AS GPR119 AGONISTS
-
Paragraph 0589-0590, (2017/10/26)
The present invention relates to novel compounds of formula (I) as GPR119 agonist, composition compositions containing such compounds and method of preparation thereof.
NEW ANTI-MALARIAL AGENTS
-
Page/Page column 16; 18-19, (2017/02/09)
The present invention is related to a use of aminopyrazine derivatives in the manufacture of a medicament for preventing or treating malaria. Specifically, the present invention is related to aminopyrazine derivatives useful for the preparation of a pharmaceutical formulation for the inhibition of malaria parasite proliferation.
Identification of a Potential Antimalarial Drug Candidate from a Series of 2-Aminopyrazines by Optimization of Aqueous Solubility and Potency across the Parasite Life Cycle
Le Manach, Claire,Nchinda, Aloysius T.,Paquet, Tanya,Gonzàlez Cabrera, Diego,Younis, Yassir,Han, Ze,Bashyam, Sridevi,Zabiulla, Mohammed,Taylor, Dale,Lawrence, Nina,White, Karen L.,Charman, Susan A.,Waterson, David,Witty, Michael J.,Wittlin, Sergio,Botha, Mari?tte E.,Nondaba, Sindisiswe H.,Reader, Janette,Birkholtz, Lyn-Marie,Jiménez-Díaz, María Belén,Martínez, María Santos,Ferrer, Santiago,Angulo-Barturen, Inìigo,Meister, Stephan,Antonova-Koch, Yevgeniya,Winzeler, Elizabeth A.,Street, Leslie J.,Chibale, Kelly
, p. 9890 - 9905 (2016/11/19)
Introduction of water-solubilizing groups on the 5-phenyl ring of a 2-aminopyrazine series led to the identification of highly potent compounds against the blood life-cycle stage of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Several compounds displayed high in vivo efficacy in two different mouse models for malaria, P. berghei-infected mice and P. falciparum-infected NOD-scid IL-2Rnull mice. One of the frontrunners, compound 3, was identified to also have good pharmacokinetics and additionally very potent activity against the liver and gametocyte parasite life-cycle stages.
MONOSUBSTITUTED DIAZABENZIMIDAZOLE CARBENE METAL COMPLEXES FOR USE IN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
-
Page/Page column 92; 93, (2015/01/16)
An organic electronic device, preferably an organic light-emitting diode (OLED), comprising at least one metal-carbene complex comprising one, two or three specific bidentate diazabenzimidazole carbene ligands;a light-emitting layer comprising said metal-carbene complex as emitter material, preferably in combination with at least one host material;the use of said metal-carbene complex in an OLED;an apparatus selected from the group consisting of stationary visual display units, mobile visual display units, illumination units, units in items of clothing, units in handbags, units in accessoires, units in furniture and units in wallpaper comprising said organic electronic device, preferably said OLED, or said light-emitting layer;the metal-carbene complex comprising one, two or three specific bidentate diazabenzimidazole carbene ligands mentioned above and a process for the preparation of said metal-carbene complex.