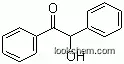
119-53-9Relevant articles and documents
THE REACTION OF PHENYLLITHIUM WITH CARBON MONOXIDE
Nudelman, N. Sbarbati,Vitale, Arturo A.
, p. 143 - 156 (1983)
Three main products are obtained from the reaction between phenyllithium and carbon monoxide, namely: benzophenone (I), benzoin (II) and α,α-diphenylacetophenone (III).Evidence is given for the existence of benzoyllithium as the first intermediate of the reaction and for the subsequent intermediates in the production of I, II and III.The basic sequences followed in the formation of those and of other minor products are outlined in the Scheme.Reaction conditions can be adjusted to obtain III in a high yield or to prevent further reaction of the first intermediate and obtain diarylalkylcarbinols, or substituted tetrahydrofurans.
Photocatalytic Coproduction of Deoxybenzoin and H2 through Tandem Redox Reactions
Luo, Nengchao,Hou, Tingting,Liu, Shiyang,Zeng, Bin,Lu, Jianmin,Zhang, Jian,Li, Hongji,Wang, Feng
, p. 762 - 769 (2020)
Photocatalytic H2 evolution from organic feedstocks with simultaneous utilization of photogenerated holes achieves solar energy storage and coproduces value-Added chemicals. Here we show visible-light H2 production from benzyl alcohol (BAL) with controllable generation of deoxybenzoin (DOB) or benzoin (BZ) through tandem redox reactions. Particularly, DOB synthesis circumvents the use of expensive feedstocks and environmentally unfriendly catalysts that are required previously. Under the irradiation of blue LEDs, the key of steering the major product to DOB rather than BZ is to decrease the conduction band bottom potentials of the ZnIn sulfide catalysts by increasing the Zn/In ratio, which results in the dehydration of intermediate hydrobenzoin (HB) to DOB proceeding in a redox-neutral mechanism and consuming an electron-hole pair. As a proof of concept, this method is used to synthesize DOB derivatives in gram scale.
-
Ohnishi,Kagami
, p. 2437 (1975)
-
-
Tanaka et al.
, p. 4979 (1972)
-
Pyridinium dichromate-assisted oxidative cleavage of α-functionalized benzylic alcohols by sodium percarbonate under phase-transfer conditions
Mohand,Levina,Muzart
, p. 2051 - 2059 (1995)
The course and the efficacy of the oxidation by sodium percarbonate of benzylic alcohols, α-substituted by a keto, hydroxy, ester or acid group, are dependent on the nature of both α-group and the solvent, and yields are usually improved by the presence of catalytic amounts of Cr(VI) species. The oxidative cleavage of the C(OH)-C(α) bond is the main process observed.
Postulation of Bis(thiazolin-2-ylidene)s as the Catalytic Species in the Benzoin Condensation Catalyzed by a Thiazolium Salt plus Base
Castells, J.,Lopez-Calahorra, F.,Domingo, L.
, p. 4433 - 4436 (1988)
Thiazolin-2-ylidenes generated by desilylation of 2-(trimethylsilyl)thiazolium ions are used as catalysts for the benzoin condensation.The experimental results together with theoretical calculations lead the postulate that bis(thiazolin-2-ylidene)s, and n
On the reactivity and stability of electrogenerated N-heterocyclic carbene in parent 1-butyl-3-methyl-1H-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate: Formation and use of N-heterocyclic carbene-CO2 adduct as latent catalyst
Feroci, Marta,Chiarotto, Isabella,Vecchio Ciprioti, Stefano,Inesi, Achille
, p. 95 - 101 (2013)
A simple electrolysis (under galvanostatic conditions) of the room temperature ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methyl-1H-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate, BMIm-BF4, yields, after bubbling CO2 into the catholyte, theadduct NHC-CO2. The considerable stability of this NHC-CO 2 adduct, at room temperature, in the parentionic liquid as solvent, has been compared with the one of free NHC in the same BMIm-BF4. The BMIm-BF4solution containing NHC-CO2 adduct, suitably triggered (US irradiation or 120 °C), is able to releasefree NHC. The NHC-CO2 adduct usefulness has been demonstrated using it as efficient latent catalyst, inBMIm-BF4as solvent, in the benzoin condensation and in the oxidative esterification of cinnamaldehydewith benzyl alcohol.
Reduction of Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Dioxide with Benzoin Carbanion. Oxygen Transfer from Products Formed by the Reduction of Sulfur Dioxide to 7,7,8,8-Tetracyanoquinodimethane
Akiyama, Fuminori
, p. 3951 - 3956 (1988)
A reaction of sulfur dioxide (SO2) with benzoin carbanion (the lithium salt of benzoin dianion, 1) in tetrahydrofuran (THF) gave a mixture of benzyl (2) and benzoin (3) in yields of 83 and 17 percent, respectively, irrespective of the reaction temperature between -78 and 25 deg C.The reaction of carbon dioxide (CO2) with 1 in THF gave a mixture of 2 and 3 accompanied by the formation of a small amount of lithium benzoate (4).The proportion of 2 in a mixture of 2 and 3 formed in the reaction of CO2 with 1 were 49, 30, and 20percent at -78, -22, and 25 deg C, respectively.The reaction of SO2 with 1 in the presence of 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) gave oligomers of TCNQ with a yield of 60percent, in which some parts of the cyano groups were transformed to carboxylato groups.
-
Solodar
, p. 287,289 (1971)
-
-
Nadkarni,Mehta
, p. 901 (1935)
-
Organocatalysis in polysiloxane gels: A magnetic-stir-bar encapsulated catalyst system prepared by thiol-ene photo-click immobilization
Yang, Hong,Xu, Ming,Guo, Ling-Xiang,Ji, Hao-Fan,Wang, Jun-Yu,Lin, Bao-Ping,Zhang, Xue-Qin,Sun, Ying
, p. 7304 - 7310 (2015)
This manuscript presents a facile thiol-ene photo-click chemistry method to prepare magnetic stir bar-encapsulated polysiloxane-based organocatalyst gels under benign conditions, and develops a Stir Bar-Encapsulated Catalysis (SBEC) technique. Through thiol-ene addition chemistry, we graft olefin-terminated organocatalysts (i.e. MacMillan catalyst, proline catalyst, and N-heterocyclic carbene catalyst) onto poly[3-mercaptopropylmethylsiloxane], which is further photo-crosslinked to coat the embedded magnetic stir bar. The prepared magnetic stir bar-encapsulated polysiloxane-based organocatalyst gels can be put into reaction flasks to perform stirring and catalysis functions at the same time. The most important benefit of SBEC technique is to infinitely simplify the catalyst/product separation procedure by using a simple stir-bar-retriever, even without any precipitation/filtration steps. The catalytic performances of three different organocatalyst gels applied in asymmetric Diels-Alder reaction, asymmetric aldol reaction and benzoin condensation reaction respectively are also examined herein.
Selective Aerobic Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohols with Palladium(0) Nanoparticles Suspension in Water
Bourbiaux, Dolorès,Mangematin, Stéphane,Djakovitch, Laurent,Rataboul, Franck
, p. 3239 - 3249 (2021)
Abstract: This study concerns one of the rare applications of a suspension of palladium nanoparticles in water for oxidation reactions. The aqueous suspension containing well dispersed nanoparticles of 3.85?nm was obtained following a straightforward procedure involving the reduction of Na2PdCl4 with NaBH4 in the presence of PVP as stabilizing agent. In the way of oxidative catalytic valorisation of lignin, the aqueous suspension was directly applied as catalytic medium for the selective oxidation of vanillic alcohol into vanillin (80?°C, O2, 1?h) with more than 90% yield. Reusability of the catalytic medium has been demonstrated, acting as “quasi-homogeneous catalyst”. More sophisticated lignin-derived substrates like veratryl alcohol and hydrobenzoin gave yields of 50–80% to the respective aldehyde and ketone. In parallel, this as-synthesized suspension was directly used to prepare a Pd/TiO2 catalyst, the latter showing less efficiency for the catalytic transformations. Graphic Abstract: [Figure not available: see fulltext.]
Photochemical Transformations of 1,2-Diketones and Benzhydrylamine
Mehrotra, Kailash Nath,Pandey, Ganesh Prasad
, p. 1081 - 1084 (1980)
Photolysis of a mixture of substituted 1,2-diketones and benzhydrylamine (in 1:2 mole ratio) in benzene gave N-benzhydrylidenebenzhydrylamine, N-(diarylmethyl)benzamides, acyloins (3), N-(arylmethylene)benzhydrylamines, and benzophenone separated by fractional crystallization and column chromatogaphy.The products have been characterised by analytical and spectral (IR, UV, and NMR) data and the structural assignments confirmed by the comparison (IR spectra and undepressed mixed mp) with authentic samples.Acyloins (3) are precursors for N-(diarylmethyl)benzamides and N-(arylmethylene)benzhydrylamines.A tentative mechanistic route for the formation of products has been suggested.
Reductive formation and transformation of epoxides in neutral aqueous medium
Kovacs, Gabor,Micskei, Karoly
, p. 9055 - 9056 (1997)
Stoichiometrically controlled reductive epoxidation could be elaborated to transform α,β-diketones or α-hydroxy ketones to epoxides in a very good yields in neutral aqueous medium using chromium(II)acetate. Modification of the coordination sphere of Cr(II) ion with the added ligand makes the reductive ring-opening possible.
Samarium diiodide promoted formation of 1,2-diketones and 1-acylamido-2-substituted benzimidazoles from N-acylbenzotriazoles
Wang, Xiaoxia,Zhang, Yongmin
, p. 4201 - 4207 (2003)
N-Acylbenzotriazoles, when treated with samarium diiodide in THF, undergo self-coupling reaction to afford 1,2-diketones in good to excellent yields; while when treated with samarium diiodide in CH3CN, they undergo ring-opening reaction to afford 1-acylamido-2-alkyl (or aryl) benzimidazoles in reasonable to good yields. A plausible mechanism was suggested.
A γ-CYCLODEXTRIN THIAZOLIUM SALT HOLOENZYME MIMIC FOR THE BENZOIN CONDENSATION
Breslow, Ronald,Kool, Eric
, p. 1635 - 1638 (1988)
Several thiazolium salts have been attached to a C-6 carbon of γ-cyclodextrin.They catalyze the benzoin condensation of benzaldehyde very effectively.
Solid-support-bound 1-aminoimidazolium chlorochromate: A selective, efficient and recyclable oxidant
Linares,Sánchez,Alajarín,Vaquero,Alvarez-Builla
, p. 382 - 388 (2001)
A series of polymer-bound imidazolium chlorochromates have been synthesised and used as selective oxidants for benzylic and cinnamylic alcohols. Solid-support-bound 1-amino-imidazolium chlorochromate proved to be the most convenient system due to its efficiency, selectivity and ease of recycling the material.
N-Heterocyclic olefins as ancillary ligands in catalysis: A study of their behaviour in transfer hydrogenation reactions
Iturmendi, Amaia,García, Nestor,Jaseer,Munárriz, Julen,Sanz Miguel, Pablo J.,Polo, Victor,Iglesias, Manuel,Oro, Luis A.
, p. 12835 - 12845 (2016)
The Ir(i) complexes [Ir(cod)(κP,C,P′-NHOPPh2)]PF6 and [IrCl(cod)(κC-NHOOMe)] (cod = 1,5-cyclooctadiene, NHOPPh2 = 1,3-bis(2-(diphenylphosphanyl)ethyl)-2-methyleneimidazoline) and NHOOMe = 1,3-bis(2-(methoxyethyl)-2-methyleneimidazoline), both featuring an N-heterocyclic olefin ligand (NHO), have been tested in the transfer hydrogenation reaction; this representing the first example of the use of NHOs as ancillary ligands in catalysis. The pre-catalyst [Ir(cod)(κP,C,P′-NHOPPh2)]PF6 has shown excellent activities in the transfer hydrogenation of aldehydes, ketones and imines using iPrOH as a hydrogen source, while [IrCl(cod)(κC-NHOOMe)] decomposes throughout the reaction to give low yields of the hydrogenated product. Addition of one or two equivalents of a phosphine ligand to the latter avoids catalyst decomposition and significantly improves the reaction yields. The reaction mechanism has been investigated by means of stoichiometric studies and theoretical calculations. The formation of the active species ([Ir(κP,C,P′-NHOPPh2)(iPrO)]) has been proposed to occur via isopropoxide coordination and concomitant COD dissociation. Moreover, throughout the catalytic cycle the NHO moiety behaves as a hemilabile ligand, thus allowing the catalyst to adopt stable square planar geometries in the transition states, which reduces the energetic barrier of the process.
VIOLOGENS THAT PLUNDER ELECTRON FROM SOLID REDUCING AGENT. REDUCTION OF ARYL KETONES BY ZINC POWDER IN THE PRESENCE OF PROPYL VIOLOGEN AS AN ELECTRON TRANSFER CATALYST
Endo, Takeshi,Saotome, Yasushi,Okawara, Makoto
, p. 4525 - 4526 (1985)
It was found that viologen (propyl viologen) acted as an Electron Transfer Catalyst (ETC) in the reduction of aryl ketones with zinc powder. α-Diketones undertook the two-electron reduction to obtain the corresponding benzoins in good yields and aromatic ketones could one-electron reduced selectively to give the corresponding pinacols.
De Novo Synthesis of α-Hydroxy Ketones by Gallic Acid-Promoted Aerobic Coupling of Terminal Alkynes with Diazonium Salts
Alcaide, Benito,Almendros, Pedro,Fernández, Israel,Herrera, Fernando,Luna, Amparo
, p. 17227 - 17230 (2017)
An unprecedented metal-free direct preparation of unprotected α-hydroxy ketones from terminal alkynes under mild conditions with diazonium salts as the arene source and without the requirement of irradiation is described. The process is general and fully compatible with a wide variety of substitution in both reactants. Experimental and computational evidence strongly suggest the involvement of radical species in the transformation.
-
Baudry,Charpentier-Morize
, p. 3013 (1973)
-
One-pot synthesis benzils from aldehydes via nhc-catalyzed benzoin dimerization under metal-free conditions in water
Bi, Xiaoxin,Wu, Lintao,Yan, Chaoguo,Jing, Xiaobi,Zhu, Hongxiang
, p. 663 - 664 (2011)
A simple and convenient one-pot procedure is reported for the synthesis of 1,2-diketones from corresponding benzoin-type condensation reaction of aromatic aldehydes in water with N,N-dialkylbenzimidazolium salt as condensation catalyst and air as oxidizing reagent.
-
Merkushev,E.B. et al.
, (1978)
-
Metal-free porous phosphorus-doped g-C3N4photocatalyst achieving efficient synthesis of benzoin
Li, Yuanjin,Wang, Shuhui,Wu, Jin,Wang, Qiuyan,Ma, Changqiu,Jiang, Daheng,Hu, Wanglai,Zhu, Lixin,Xu, Xiaoliang
, p. 12682 - 12686 (2021)
Photocatalytic organic synthesis is mostly limited by the shortcomings of insufficient light absorption, high photogenerated electron-hole recombination rate and inadequate reactive sites of photocatalysts. To solve these problems, phosphorus-doped g-C3N4with a porous structure was constructed. Benefiting from enhanced light absorption and electron-hole separation efficiency, PCNT has intensive oxygen activation ability to generate superoxide radicals, and is highly active in organic synthesis. In addition, PCNT has enhanced surface nucleophilicity, which is conducive to the carbon-carbon coupling process of the intermediate product benzaldehyde molecules and benzyl alcohol molecules in the benzoin condensation reaction. Metal-free PCNT is expected to replace the previously used highly toxic cyanide catalysts and provide a new way for the low-cost and efficient photocatalytic synthesis of benzoin.
Synthesis, structure and oxidation of alkynes using a μ-oxo diiron complex with the ligand bis (1-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-benzimidazol-2-yl methyl) ether
Khattar, Raghvi,Hundal,Mathur, Pavan
, p. 129 - 134 (2012)
New ligand bis (1-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl ether and its μ-oxo diferric complex has been synthesized and characterized. The dimeric [LClFe-O-FeCl3] has been characterized crystallographically, and shows that iron atoms occupy inequivalent coordination sites. One of the Fe (III) atom is coordinated by two benzimidazole nitrogens, one ether oxygen and bridging oxide oxygen, forming the equatorial plane while one Cl- ion and the oxygen atom of a DMF molecule occupy the axial fifth and the sixth coordination positions. The second Fe (III) is tetrahedrally coordinated by three Cl- ions and the bridging oxide oxygen O. The bridging oxide anion is unsymmerically coordinated to the two Iron (III) atoms. Oxidation of aromatic alkynes was investigated using this complex as catalyst with small amount of tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) and Hydrogen peroxide (H 2O2) as an alternate source of oxygen. Isolated products were characterized by GC-Mass. Solvent, temperature, Stoichiometry and oxidant variation are studied and reaction conditions have been optimized. Dicarbonyl and α,β-acetylenic ketone are the major product and depend on the nature of the alkyne employed.
Generation and reactivity of phenylhydroxycarbenes in solution
Keul, Felix,Mardyukov, Artur,Schreiner, Peter R.
supporting information, (2022/01/19)
We provide evidence for the first successful generation of phenylhydroxycarbene and 4-trifluoromethylphenylhydroxycarbene in solution. The carbene tautomers of the corresponding benzaldehyde derivatives had been prepared under cryogenic matrix-isolation conditions before but their reactivity, apart from a prototypical quantum mechanical tunneling [1,2]-H-shift reaction, had not been studied. Here our strategy is to employ suitable carbene precursors for the McFadyen–Stevens reaction, to generate the parent and the para-CF3-substituted phenylhydroxycarbenes, and to react them with benzaldehyde or acetone in a highly facile, allowed six-electron carbonyl-ene reaction toward the corresponding α-hydroxy ketones. Our findings are supported by computations at the DLPNO-CCSD(T)/cc-pVQZ//B3LYP/def2-TZVP level of theory.
Visible Light Enabled Formal Cross Silyl Benzoin Reaction as an Access to α-Hydroxyketones
Ma, Liyao,Yu, Yinghua,Xin, Luoting,Zhu, Lei,Xia, Jiajin,Ou, Pengcheng,Huang, Xueliang
supporting information, p. 2573 - 2577 (2021/04/05)
In this work, a visible-light enabled coupling of acylsilanes with aldehydes to give a range of cross-benzoin type products α-hydroxyketones is described. The reaction could proceed at ambient temperature, with the irradiation of low energy visible light, and without addition of photosensitizer or any other additives. (Figure presented.).
Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of α-aryl acetophenones from styryl ethers and aryl diazonium saltsviaregioselective Heck arylation at room temperature
Kandasamy, Jeyakumar,Lee, Yong Rok,Singh, Adesh Kumar,Venkatesh, Rapelly
supporting information, p. 7832 - 7837 (2021/09/28)
Preparation of α-aryl acetophenones from styryl ethers and aryldiazonium salts is described. The reaction is catalyzed by palladium acetate at room temperature in the absence of ligand and base. The developed method is highly attractive in terms of reaction conditions, substrate scope, functional group tolerance and yields. Synthetic applications of the present method are demonstrated by preparing α-aryl indoles and 3-aryl isocoumarin from styryl ethers.